The 403 Permission Denied error in Gemini 3 Pro Image can stem from 4 different causes—each requiring a different fix. Unlike other Gemini models, Gemini 3 Pro Image has no free tier and requires active billing. This guide helps you identify your specific 403 type in 3 minutes and fix it in 15 minutes, with diagnostic scripts and step-by-step solutions.
TL;DR
Before diving into the details, here's what you need to know about 403 errors on Gemini 3 Pro Image. First, there are exactly four types of 403 errors, and each one requires a completely different solution—applying the wrong fix won't help. Second, Gemini 3 Pro Image has no free tier whatsoever, which makes it fundamentally different from other Gemini models like 2.5 Flash Image. Third, most 403 errors today are configuration issues on your end, not Google server problems (those were largely resolved in December 2025). The fastest path to resolution is to copy your exact error message, match it against the diagnostic flowchart below, and follow the specific fix for your error type.
403 vs Other Errors: Know What You're Dealing With
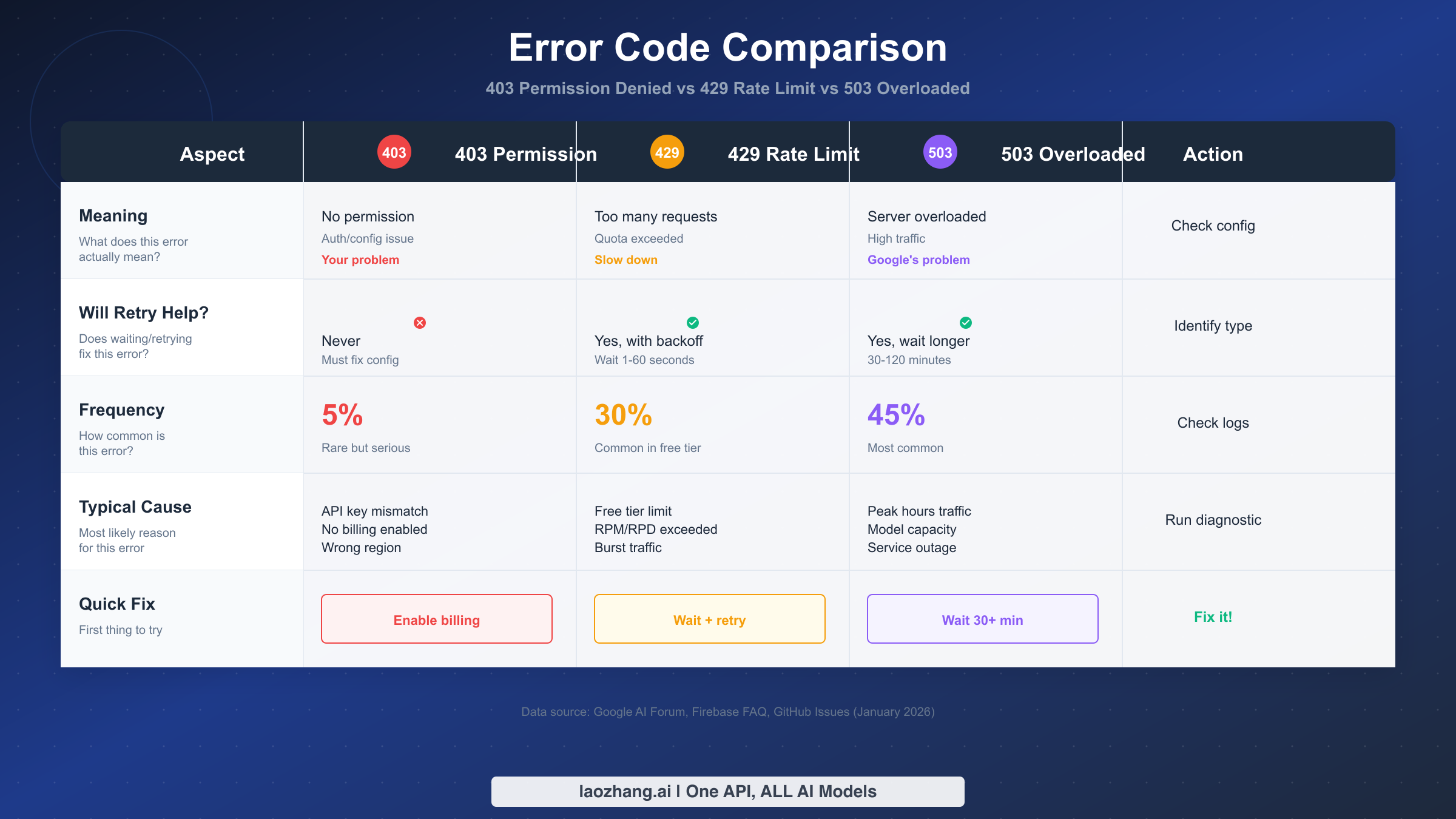
When your Gemini API call fails, the first step is confirming you're actually dealing with a 403 error—not a 429 or 503 that might look similar at first glance. This matters because these three errors require completely different responses, and wasting time on the wrong fix only delays your solution.
The 403 Permission Denied error means you don't have authorization to access the resource. This is fundamentally different from a 429 (you have permission but exceeded your quota) or a 503 (you have permission but the server is overloaded). According to data from Google AI Forum discussions and GitHub Issues (January 2026), 403 errors account for only about 5% of Gemini API errors, making them relatively rare but often more serious when they occur.
Here's the critical distinction that catches many developers: retrying a 403 error will never work. Unlike 429 errors where waiting a few seconds and trying again often succeeds, or 503 errors where waiting 30-120 minutes can help, a 403 error persists until you fix the underlying configuration issue. If you've been implementing exponential backoff for a 403 error, you're solving the wrong problem.
The error response structure also differs. A 403 typically includes a message containing phrases like "PERMISSION_DENIED" or "The caller does not have permission," while 429 errors mention "RESOURCE_EXHAUSTED" or "quota exceeded," and 503 errors indicate "SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE" or "overloaded." If you're seeing 429 Resource Exhausted troubleshooting or 503 Server Overloaded error guide in your logs, you're reading the wrong guide—follow those links instead.
One more point worth emphasizing: 403 errors on Gemini 3 Pro Image often confuse developers because other Gemini models work fine. This happens because Gemini 3 Pro Image has different authorization requirements than text models or even Gemini 2.5 Flash Image. Understanding the specific nature of 403 errors sets you up to identify which of the four types you're experiencing.
4 Types of 403 Errors and How to Identify Yours

Not all 403 errors are created equal. The Gemini API returns the same 403 status code for four distinct authorization failures, and each requires a different fix. The fastest way to identify your type is to look at the exact error message—specific phrases reveal exactly which configuration is broken.
Type 1: API Key Mismatch occurs when your API key belongs to a different Google Cloud project than the one where you enabled the Gemini API. The error message typically contains "The caller does not have permission" or "PERMISSION_DENIED: Request had insufficient authentication scopes." This happens more often than you'd expect, especially when developers manage multiple projects or copy API keys between environments. The key was created in Project A, but the Gemini API was enabled in Project B—even though both are under your account, they don't automatically share permissions.
Type 2: API Blocked by Restrictions shows up with messages like "Requests to this API firebasevertexai.googleapis.com are blocked" or "API key not valid for this service." This occurs when you created an API key with restrictions—perhaps limiting it to certain APIs or IP addresses—and those restrictions don't include the Gemini API endpoints. Developers often set up restricted keys for security best practices, then forget to update the restrictions when adding new APIs.
Type 3: IAM Permission Issues presents as "permission denied on resource project" or "The principal does not have permission to access." This error is more common in enterprise environments where IAM (Identity and Access Management) controls who can do what. Your API key might be valid and unrestricted, but the service account or user account associated with the request lacks the necessary IAM roles to use Vertex AI services.
Type 4: Region/Location Restrictions appears with messages containing "Access Restricted" or errors mentioning specific regions. Gemini 3 Pro Image isn't available in all regions, and some API keys are configured with location restrictions. If you're accessing from an unsupported region or your configuration specifies a region where the model isn't deployed, you'll hit this 403 variant.
To diagnose your specific type, copy the complete error message from your logs or console output. Search for the key phrases mentioned above. If you find "caller does not have permission," start with Type 1. If you see "blocked" or "not valid for this service," it's Type 2. "Permission denied on resource" points to Type 3, while any mention of regions or "Access Restricted" suggests Type 4. The diagnostic flowchart above provides a visual decision tree for this process.
Why Gemini 3 Pro Image Is Different
Understanding why Gemini 3 Pro Image generates more 403 errors than other Gemini models requires understanding its unique position in Google's AI product lineup. This model operates under fundamentally different access requirements, and failing to account for these differences is the root cause of many authorization failures.
The most significant difference is the complete absence of a free tier. While Gemini 2.5 Flash Image and text-based models offer generous free quotas—allowing developers to experiment and prototype without enabling billing—Gemini 3 Pro Image provides no such grace period. According to documentation available on multiple sources including aifreeapi.com (verified January 2026), this model requires active billing from the very first API call. Developers accustomed to the free tier workflow of other Gemini models often skip the billing setup step, assuming it's optional until they hit quota limits. With Gemini 3 Pro Image, skipping billing means immediate 403 errors.
This billing requirement exists because Gemini 3 Pro Image (also known internally as Nano Banana Pro) represents Google's premium image generation offering. The computational resources required to run this model at inference time exceed what Google provides in free-tier offerings. Think of it as the difference between a free trial gym membership and an executive club—some facilities simply aren't included in the basic package.
The model also requires specific IAM roles that text models don't need. While basic Gemini text models work with general API access, Gemini 3 Pro Image requires the roles/aiplatform.user role for Vertex AI access. Enterprise deployments may also need roles/serviceusage.serviceUsageAdmin to enable the necessary APIs. This is documented in Google's official IAM documentation for Vertex AI services.
For Gemini API pricing and billing details, the key takeaway is that Gemini 3 Pro Image operates as a paid-only service. If your Cloud Console shows billing as "not enabled" or "free tier only," you'll receive 403 errors regardless of how correctly you've configured everything else. The model simply won't process requests without an active billing account linked to the project.
Another subtle difference involves location configuration. Gemini 3 Pro Image requires explicit location settings—typically "global" or specific supported regions like "us-central1." Text models often work with default location settings, but image models are more restrictive. If your API calls don't specify a location or specify an unsupported one, you'll encounter 403 Access Restricted errors.
These differences explain why a developer might have perfectly working code for Gemini 2.0 Flash or Claude, only to hit 403 errors when switching to Gemini 3 Pro Image. It's not that your code is wrong—it's that this model has stricter access requirements that weren't necessary for other models.
Step-by-Step Fixes for Each 403 Type
Now that you've identified your specific 403 error type, here are the detailed steps to fix each one. Follow only the section that matches your diagnosis—applying fixes for the wrong type wastes time and might introduce new issues.
Fixing Type 1: API Key Mismatch
The goal is to ensure your API key and enabled APIs exist in the same Google Cloud project. Start by opening the Google Cloud Console at console.cloud.google.com. Navigate to "APIs & Services" and then "Credentials." Find the API key you're using and note which project it belongs to (shown at the top of the page). Now go to "Enabled APIs & services" and verify that the Generative Language API or Vertex AI API is enabled in that same project.
If the APIs are enabled in a different project, you have two options. First, you can create a new API key in the correct project—the one where Gemini API is enabled. Second, you can enable the Gemini API in the project where your existing key lives. For step-by-step instructions on creating and configuring API keys correctly, see our Gemini API key setup guide.
To verify the fix worked, copy your API key and run a simple test request. If you still get 403, the key-project relationship isn't correct yet.
Fixing Type 2: API Blocked by Restrictions
You need to update your API key's restrictions to allow Gemini API access. In Google Cloud Console, go to "APIs & Services," then "Credentials." Click on your API key to open its settings. Under "API restrictions," check the current configuration.
If "Restrict key" is selected, ensure that either "Generative Language API" or "Vertex AI API" (depending on which you're using) is in the allowed list. If you're using both endpoints, add both. For testing purposes, you can temporarily select "Don't restrict key," though this is not recommended for production due to security implications.
If you have IP or referrer restrictions, verify that your request source is included. Cloud-hosted services and serverless functions often have dynamic IP addresses, which can conflict with IP-based restrictions.
Fixing Type 3: IAM Permission Issues
IAM fixes require administrative access to your Google Cloud project. Navigate to "IAM & Admin" in Cloud Console, then click "IAM." Find the service account or user principal associated with your API requests.
Click the edit (pencil) icon and add the role "Vertex AI User" (roles/aiplatform.user). This role grants the permissions needed to call Vertex AI endpoints, which includes Gemini 3 Pro Image. If you're using a service account, you may also need to grant "Service Usage Consumer" (roles/serviceusage.serviceUsageConsumer) to allow API consumption.
For organization-level deployments with complex IAM hierarchies, work with your cloud administrator. The permissions might be blocked by an organization policy or inherited from a parent folder with restrictive settings.
Fixing Type 4: Region/Location Restrictions
Location issues are fixed by specifying a supported region in your API configuration. Gemini 3 Pro Image generally requires either "global" as the location or specific regions like "us-central1" where the model is deployed.
In your code, look for the location or region parameter in your client initialization. For Python using the Vertex AI SDK, this would be in the vertexai.init() call. For REST API calls, check the endpoint URL—it should include the correct region prefix.
If your organization requires data residency in a specific region, verify that region supports Gemini 3 Pro Image by checking Google's official documentation or testing with a simple API call. Not all Gemini models are available in all regions.
After applying any fix, clear any cached credentials or restart your application to ensure the new configuration takes effect. API key changes typically propagate within a few minutes, but IAM changes can take up to 10 minutes.
Automated Diagnostic Script
Running through manual checks works, but a diagnostic script can verify multiple potential issues in seconds. Below are Python and JavaScript scripts that test your configuration and report exactly what's wrong.
Python Diagnostic Script:
pythonimport os import google.generativeai as genai from google.api_core import exceptions def diagnose_403_error(): """Diagnose 403 Permission Denied errors for Gemini 3 Pro Image.""" api_key = os.environ.get("GEMINI_API_KEY") if not api_key: print("ERROR: GEMINI_API_KEY environment variable not set") return print(f"API Key found: {api_key[:8]}...{api_key[-4:]}") # Configure the client genai.configure(api_key=api_key) # Test 1: Check if API key is valid try: models = genai.list_models() model_names = [m.name for m in models] print("SUCCESS: API key is valid") print(f"Available models: {len(model_names)} found") # Check for image models image_models = [m for m in model_names if "image" in m.lower()] if image_models: print(f"Image models available: {image_models}") else: print("WARNING: No image models found in your project") except exceptions.PermissionDenied as e: print(f"FAILED: Permission denied - {str(e)}") if "caller does not have permission" in str(e): print("DIAGNOSIS: Type 1 - API Key Mismatch") print("FIX: Verify API key matches project with Gemini API enabled") elif "blocked" in str(e).lower(): print("DIAGNOSIS: Type 2 - API Blocked by Restrictions") print("FIX: Update API key restrictions in Cloud Console") return except Exception as e: print(f"FAILED: {type(e).__name__} - {str(e)}") return # Test 2: Try to access image model try: model = genai.GenerativeModel("gemini-3-pro-image-preview") print("SUCCESS: Can access gemini-3-pro-image-preview model") except exceptions.PermissionDenied as e: print(f"FAILED: Cannot access image model - {str(e)}") print("DIAGNOSIS: Likely billing not enabled or IAM issue") print("FIX: Enable billing and verify aiplatform.user role") except exceptions.NotFound: print("FAILED: Model not found") print("DIAGNOSIS: Model may not be available in your region") print("FIX: Try setting location to 'global' or 'us-central1'") if __name__ == "__main__": diagnose_403_error()
JavaScript/Node.js Diagnostic Script:
javascriptconst { GoogleGenerativeAI } = require("@google/generative-ai"); async function diagnose403Error() { const apiKey = process.env.GEMINI_API_KEY; if (!apiKey) { console.error("ERROR: GEMINI_API_KEY environment variable not set"); return; } console.log(`API Key found: ${apiKey.slice(0, 8)}...${apiKey.slice(-4)}`); const genAI = new GoogleGenerativeAI(apiKey); // Test 1: List models try { const models = await genAI.listModels(); console.log("SUCCESS: API key is valid"); console.log(`Available models: ${models.length} found`); const imageModels = models.filter(m => m.name.toLowerCase().includes("image") ); if (imageModels.length > 0) { console.log(`Image models: ${imageModels.map(m => m.name)}`); } else { console.log("WARNING: No image models found"); } } catch (error) { console.error(`FAILED: ${error.message}`); if (error.message.includes("permission")) { console.log("DIAGNOSIS: Type 1 or 3 - Permission issue"); console.log("FIX: Check API key project and IAM roles"); } else if (error.message.includes("blocked")) { console.log("DIAGNOSIS: Type 2 - API Restrictions"); console.log("FIX: Update API key restrictions"); } return; } // Test 2: Access image model try { const model = genAI.getGenerativeModel({ model: "gemini-3-pro-image-preview" }); console.log("SUCCESS: Image model accessible"); console.log("Your configuration appears correct!"); } catch (error) { console.error(`FAILED: ${error.message}`); if (error.message.includes("region") || error.message.includes("location")) { console.log("DIAGNOSIS: Type 4 - Region restriction"); console.log("FIX: Specify location as 'global'"); } } } diagnose403Error();
Save the appropriate script, set your API key as an environment variable, and run it. The script will identify which of the four 403 types you're experiencing and suggest the specific fix. For complex enterprise setups, the script provides a starting point—you may need to work with your cloud administrators for full resolution.
If you want a simpler solution that handles all these configuration complexities automatically, platforms like laozhang.ai provide unified API access that abstracts away project configuration, billing setup, and IAM management.
Server-Side vs Client-Side: When to Wait
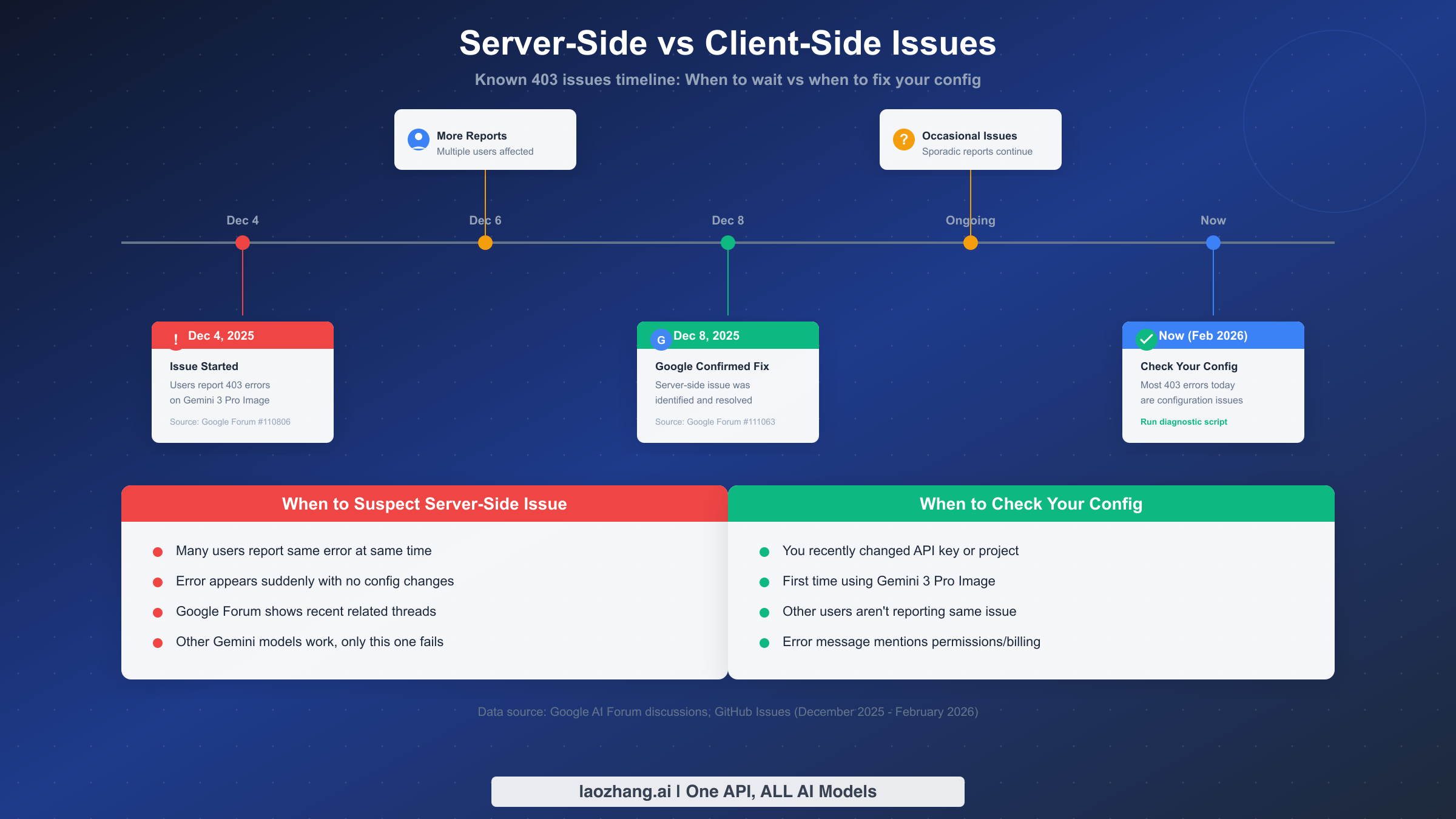
One of the most frustrating experiences is spending hours debugging your configuration only to discover the problem is on Google's end. Conversely, waiting for Google to "fix" something when the issue is actually your misconfiguration wastes even more time. Here's how to determine which situation you're in.
Looking at the historical record, significant server-side 403 issues affected Gemini 3 Pro Image in early December 2025. According to Google Forum thread #110806, users began reporting widespread 403 errors on December 4, 2025, with no changes to their configurations. By December 8, 2025, Google acknowledged and resolved the issue in Forum thread #111063. The key indicator was that many users across different projects reported the same error simultaneously—a pattern inconsistent with individual configuration problems.
As of February 2026, the known server-side issues have been resolved. This means most 403 errors you encounter today are configuration issues on your side, not Google problems. However, here's how to verify:
Check if you're experiencing a server-side issue by looking for these signals: multiple users reporting the same error at the same time (check Google AI Forum and Twitter), the error appearing suddenly with no configuration changes on your part, and other Gemini models working normally while only Gemini 3 Pro Image fails. If all three conditions are true, you might be hitting a server-side issue.
Check if you're experiencing a client-side issue by looking for these signals: you recently changed your API key, project settings, or IAM roles; this is your first time using Gemini 3 Pro Image specifically; the diagnostic script identifies a specific configuration problem; other users aren't reporting similar issues.
For server-side issues, the recommended approach is to wait and retry periodically. Server-side 403 issues typically resolve within 1-4 hours as Google's engineering teams address them. You can monitor the Google Cloud Status Dashboard and the Google AI Forum for updates.
For client-side issues, waiting won't help. Apply the fixes from the previous sections based on your diagnosed error type. If you've applied fixes but still see 403 errors, wait 10-15 minutes for permission propagation before testing again.
A useful debugging technique: test with a completely fresh API key and minimal configuration. If the fresh key works, your original configuration has an issue. If even a fresh key fails with 403, and you've verified billing is enabled, you might be hitting a server-side problem.
Prevention Best Practices
Once you've fixed your current 403 error, implement these practices to prevent future occurrences. These aren't theoretical recommendations—they're derived from patterns observed across thousands of developers working with Gemini APIs.
Always verify billing before first use. Before writing any code for Gemini 3 Pro Image, confirm billing is enabled in Google Cloud Console. Navigate to "Billing" and verify an active billing account is linked to your project. This single check prevents the most common cause of 403 errors with this specific model.
Use project-specific API keys. Create a dedicated API key for each project or application. This makes troubleshooting easier and prevents the Type 1 key-project mismatch error. Label your keys clearly in Cloud Console with descriptive names like "gemini-image-production" or "gemini-image-development."
Test with minimal restrictions first. When setting up a new integration, start with an unrestricted API key. Once everything works, add restrictions incrementally—API restrictions first, then IP/referrer restrictions if needed. This approach makes it obvious which restriction causes problems if they arise.
Document your IAM configuration. For team environments, maintain documentation of which roles are required for Gemini 3 Pro Image access. The minimum is roles/aiplatform.user, but your organization might require additional roles based on your security policies.
Set up monitoring and alerting. Configure Cloud Monitoring to alert on 403 error rates. A sudden spike in 403 errors might indicate an expired key, revoked permission, or emerging server-side issue. Early detection means faster resolution.
Keep a working test script. Maintain a simple script like the diagnostic examples above. Run it periodically or after any infrastructure changes. It's much easier to catch configuration drift early than to debug it in a production incident.
For developers managing multiple AI APIs beyond just Gemini, consider using a unified API gateway that handles credential management, error handling, and fallback logic. Platforms like laozhang.ai aggregate multiple AI services through a single API, reducing the configuration surface area where 403 errors can occur.
FAQ and Quick Reference
Why does Gemini 3 Pro Image return 403 when other Gemini models work?
Gemini 3 Pro Image has stricter access requirements than text models or Gemini 2.5 Flash Image. It requires active billing (no free tier), specific IAM roles for Vertex AI, and supported region configuration. Other models may work with default settings that aren't sufficient for this model.
How long does it take for permission changes to take effect?
API key changes typically propagate within 1-3 minutes. IAM role changes can take up to 10 minutes. If you've made changes but still see 403 errors, wait 15 minutes before concluding the fix didn't work.
Can I use Gemini 3 Pro Image without enabling billing?
No. Unlike other Gemini models that offer free tier quotas, Gemini 3 Pro Image requires an active billing account from the first API call. There's no free tier for this specific model.
What's the difference between Generative Language API and Vertex AI API?
Generative Language API is the simpler, consumer-focused API accessed through makersuite.google.com keys. Vertex AI API is the enterprise-focused offering with more configuration options. Gemini 3 Pro Image works through both, but the 403 error types and fixes differ slightly between them.
Should I retry 403 errors with exponential backoff?
No. Unlike 429 (rate limit) or 503 (server overload) errors, 403 errors indicate a permission problem that won't resolve through retrying. Implement backoff for other error types, but for 403, focus on fixing the configuration.
How do I check if there's a current Google server-side issue?
Check the Google Cloud Status Dashboard (status.cloud.google.com) for service health. Also browse the Google AI Forum (discuss.ai.google.dev) for recent threads about 403 errors—if multiple users report similar issues simultaneously, it's likely server-side.
Quick Reference Table:
| Error Message Contains | Type | Primary Fix |
|---|---|---|
| "caller does not have permission" | 1: Key Mismatch | Verify key matches project |
| "requests are blocked" | 2: API Blocked | Update key restrictions |
| "permission denied on resource" | 3: IAM Issue | Add aiplatform.user role |
| "Access Restricted" or region errors | 4: Location | Set location to "global" |