Clawdbot has emerged as one of the most exciting open-source projects of 2026, amassing over 52,900 GitHub stars in just weeks. While most users default to Claude as their LLM backend, Google Gemini offers a compelling alternative with its generous free tier, 1M token context window, and multimodal capabilities. This guide provides everything you need to integrate Gemini with Clawdbot, from initial setup through advanced optimization strategies.
TL;DR
Clawdbot supports Google Gemini as an alternative to Claude through a simple two-command setup. Enable the plugin with clawdbot plugins enable google-gemini-cli-auth, then authenticate using clawdbot models auth login --provider google-gemini-cli --set-default. Gemini's free tier provides 5-15 requests per minute with up to 1M token context, making it ideal for cost-conscious users. The paid tier starts at just $0.10 per million input tokens for Flash-Lite, significantly cheaper than Claude alternatives. This guide covers complete setup instructions, model selection strategies, real cost comparisons, and security best practices.
What is Clawdbot and Why Choose Gemini?
Clawdbot represents a fundamental shift in how we interact with AI assistants. Unlike traditional chatbots confined to web browsers or mobile apps, Clawdbot is a self-hosted, open-source personal AI that runs directly on your hardware and connects to the messaging platforms you already use daily, including Discord, WhatsApp, Telegram, Slack, iMessage, and Microsoft Teams. Created by Peter Steinberger, this project has captured the attention of developers worldwide with its combination of power, flexibility, and the playful lobster mascot that has become its signature.
The architecture of Clawdbot consists of two main components that work in harmony. First, there is an LLM-powered agent that runs on your computer, capable of using multiple language models including Claude, Gemini, GPT, and local options through LM Studio. Second, a gateway serves as the bridge between your messaging apps and the agent, allowing you to communicate through whatever platform feels most natural. This design means your AI assistant is always available wherever you are, without switching contexts or opening separate applications.
Google Gemini brings several compelling advantages as your Clawdbot backend. The most immediately attractive feature is the generous free tier that requires no credit card and provides genuine utility for moderate usage patterns. Gemini offers 5 to 15 requests per minute depending on the model, 250,000 tokens per minute throughput, and up to 1,000 requests per day for certain models. Perhaps most impressively, Gemini models support a 1 million token context window, dwarfing the 200,000 token limit of Claude models and enabling entirely new use cases for document analysis and long-running conversations.
The multimodal capabilities of Gemini extend beyond text to include native support for images, audio, and video processing. This means your Clawdbot assistant can analyze screenshots you share, transcribe voice messages, and even process video content directly. For users building assistants that need to work with diverse content types, Gemini provides capabilities that would require multiple separate services with other providers.
Prerequisites and Environment Setup
Before diving into Gemini integration, you need to ensure your environment meets Clawdbot's requirements and understand some important considerations about Gemini's availability. The foundation of a successful setup starts with proper preparation, and addressing potential issues upfront will save significant troubleshooting time later.
System Requirements
Clawdbot has modest but specific hardware requirements that determine what you can run effectively. The absolute minimum gateway specification includes a single vCPU, 1GB of RAM, and approximately 500MB of disk space. However, the recommended configuration for comfortable operation with multiple messaging channels calls for 2GB of RAM and provides better headroom for logs, media processing, and concurrent connections. On the software side, Node.js version 22 or higher is mandatory, as Clawdbot relies on modern JavaScript features that older versions do not support.
The platform supports macOS, Linux, and Windows through WSL2, with Linux (particularly Ubuntu LTS or modern Debian derivatives) being the preferred choice for server deployments. For local development and personal use, macOS works excellently, and many users run Clawdbot on Mac Mini devices for always-on availability. The project documentation explicitly notes that Bun is not recommended for gateway deployments due to compatibility concerns, so stick with Node and npm or pnpm for the most reliable experience.
Regional Considerations
An important limitation affects users in certain regions. Google's Gemini API terms require that applications serving users in the European Economic Area, Switzerland, or the United Kingdom must use paid services only, meaning the free tier is not available for those locations. If you're building an assistant primarily for personal use in these regions, you'll need to factor in API costs from the start, or consider whether the free tier restrictions create compliance concerns for your use case. For a detailed analysis of regional availability, our guide on Gemini regional restrictions provides comprehensive coverage of this topic.
Node.js Installation
Installing the correct Node.js version forms the foundation of your Clawdbot setup. The recommended approach uses a version manager like nvm (Node Version Manager) which allows easy switching between Node versions and avoids permission issues with global packages. Start by installing nvm if you haven't already, then install and use Node 22 with the commands nvm install 22 followed by nvm use 22. Verify your installation with node --version which should display v22.x.x or higher. For users who prefer system-wide installation, the official Node.js website provides installers for all platforms, and package managers like Homebrew on macOS or apt on Ubuntu can install recent Node versions. Whatever method you choose, confirm the version before proceeding, as Clawdbot will fail to start on older Node releases with confusing error messages about unsupported syntax or missing APIs.
Clawdbot Installation
With Node properly configured, installing Clawdbot globally takes a single command: npm install -g clawdbot@latest. This installs the latest stable version and makes the clawdbot command available system-wide. After installation, run clawdbot --version to confirm success and clawdbot doctor to check your configuration and identify any potential issues before proceeding.
The initial onboarding wizard streamlines configuration significantly. Running clawdbot onboard --install-daemon launches an interactive process that walks you through setting up your AI model, configuring working directories, enabling messaging channels, and installing the daemon for always-on operation. While this wizard covers basic configuration, we'll be customizing the Gemini setup more specifically in the following sections.
Step-by-Step Gemini Integration
Now we arrive at the core of this guide: actually connecting Gemini to your Clawdbot installation. Unlike some providers that use simple API keys, Gemini uses an OAuth plugin authentication flow that provides better security through token refresh and proper credential management. This approach stores OAuth tokens in auth profiles on your gateway host, automatically handling token expiration and renewal.
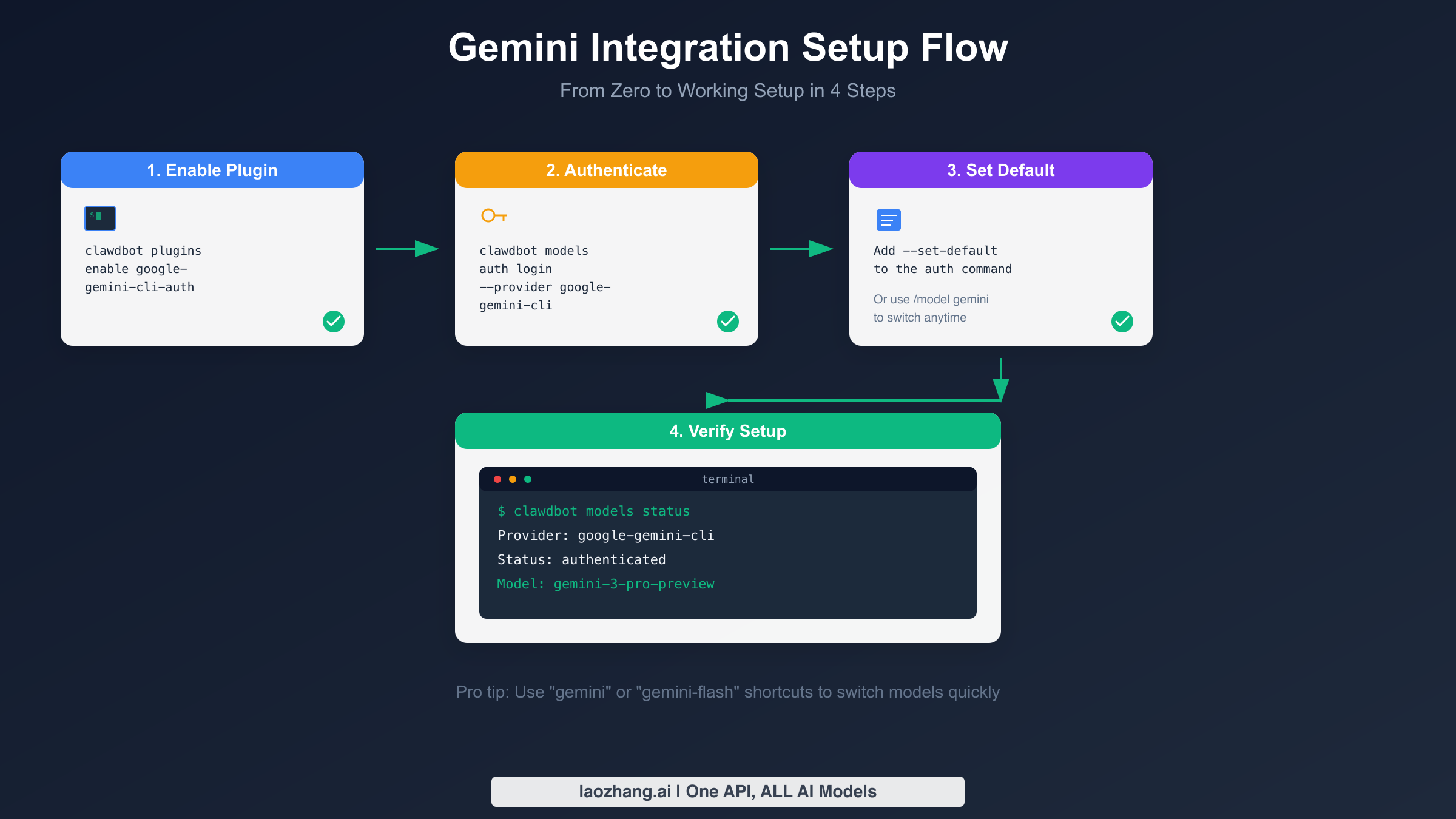
Enabling the Gemini Plugin
The first step enables the authentication plugin that handles Gemini's OAuth flow. Open your terminal and run the following command:
bashclawdbot plugins enable google-gemini-cli-auth
This command registers the Gemini authentication plugin with your Clawdbot installation, preparing it to handle the OAuth handshake with Google's servers. The plugin approach differs from traditional API key storage and provides advantages for security-conscious users who prefer not to have long-lived credentials stored in configuration files.
After enabling the plugin, you can verify it's active by listing installed plugins with clawdbot plugins list. You should see google-gemini-cli-auth in the output with an enabled status. If the plugin doesn't appear or shows as disabled, retry the enable command and check for any error messages that might indicate permission or connectivity issues.
Authenticating with Google
With the plugin enabled, the next step authenticates your Google account and grants Clawdbot permission to use the Gemini API on your behalf. Execute the authentication command:
bashclawdbot models auth login --provider google-gemini-cli --set-default
This command initiates an OAuth flow that typically opens a browser window where you'll sign into your Google account and approve the requested permissions. The --set-default flag tells Clawdbot to use Gemini as your primary model provider after successful authentication, saving you from manually switching later. If you're running Clawdbot on a headless server without a browser, the command will provide a URL you can open on another device to complete authentication.
The OAuth tokens retrieved during this process are stored securely in your Clawdbot configuration directory, typically at ~/.clawdbot/. These tokens have limited lifespans and the plugin automatically refreshes them before expiration, so you won't need to re-authenticate under normal circumstances. If you ever need to remove or reset authentication, the command clawdbot models auth logout --provider google-gemini-cli clears your stored credentials.
Verifying Your Setup
After completing authentication, verify everything is working correctly by checking your model status:
bashclawdbot models status
You should see output confirming the google-gemini-cli provider is authenticated and showing your current model selection. If the status shows any authentication errors, try logging out and back in, and ensure your network connection allows access to Google's OAuth endpoints.
For a quick functional test, you can send a simple message through Clawdbot to confirm Gemini is responding. Use the command clawdbot chat "Hello, which AI model are you?" and verify you receive a response identifying as a Gemini model. This end-to-end test confirms not just authentication but actual message processing through the Gemini API.
Configuration Options
While the default configuration works for most users, you can customize Gemini settings by editing the configuration file at ~/.clawdbot/clawdbot.json. The agent section controls model selection and behavior:
json{ "agent": { "model": "google/gemini-3-pro-preview" } }
For users who prefer environment variables over configuration files, you can set GEMINI_API_KEY if you have a traditional API key instead of using OAuth authentication. However, the OAuth flow generally provides better security and automatic token management, so we recommend sticking with the plugin approach unless you have specific requirements for API key usage.
Understanding Gemini Models in Clawdbot
Choosing the right Gemini model significantly impacts both your experience and your costs. Google offers multiple Gemini variants optimized for different use cases, and Clawdbot provides convenient shortcuts for the most commonly used options. Understanding these models helps you make informed decisions about which to use for various tasks.
Available Models and Shortcuts
Clawdbot includes built-in shortcuts that map to full Gemini model names, making it easy to switch models without typing lengthy identifiers. The shortcut gemini maps to google/gemini-3-pro-preview, the latest and most capable model, while gemini-flash maps to google/gemini-3-flash-preview, the speed-optimized variant. You can switch between models mid-session using the /model command followed by the shortcut name, without restarting Clawdbot or losing conversation context.
The Gemini 3 Pro Preview represents Google's flagship model with the strongest reasoning capabilities, best performance on complex tasks, and highest quality outputs. It supports the full 1 million token context window and handles multimodal inputs including text, images, audio, and video. The trade-off comes in speed and cost, as this model processes requests more slowly and costs more than lighter alternatives.
Gemini 3 Flash Preview prioritizes speed while maintaining good quality for most tasks. It processes requests significantly faster than Pro, making it ideal for interactive applications where responsiveness matters. The cost is also lower, and many users find Flash sufficient for routine tasks while reserving Pro for complex analysis or creative work.
For users prioritizing cost above all else, Gemini 2.5 Flash-Lite offers remarkably low pricing at just $0.10 per million input tokens. While not as capable as the newer Gemini 3 models, Flash-Lite handles basic tasks competently and can dramatically reduce costs for high-volume usage. Consider using Flash-Lite for simple queries and automated tasks while routing complex requests to more capable models.
Model Selection Strategy
Developing a strategy for model selection helps optimize both cost and quality. For everyday personal assistant tasks like reminders, simple questions, and basic automation, Gemini Flash or even Flash-Lite provides adequate performance at minimal cost. When you need deep analysis, complex reasoning, or high-quality creative output, switching to Gemini Pro justifies the additional expense.
Some users implement automated model routing based on task complexity, though this requires additional configuration. A simpler approach uses the /model command to manually switch when you know a task requires more capability. For example, before asking Clawdbot to analyze a lengthy document or debug complex code, switch to Pro mode, then return to Flash for routine interactions.
The context window advantage of Gemini deserves special consideration. With 1 million tokens available, you can include entire codebases, lengthy documents, or extended conversation histories that would be impossible with Claude's 200,000 token limit. This enables use cases like analyzing complete repositories, processing long-form content without chunking, and maintaining coherent conversations over extended periods.
Cost Analysis: Gemini vs Claude for Clawdbot
Cost represents one of the most compelling reasons to consider Gemini over Claude for your Clawdbot backend. While Claude models offer excellent quality, their pricing structure makes heavy usage expensive. Gemini provides a generous free tier and significantly lower paid rates, potentially saving hundreds of dollars monthly for active users.
Pricing Breakdown
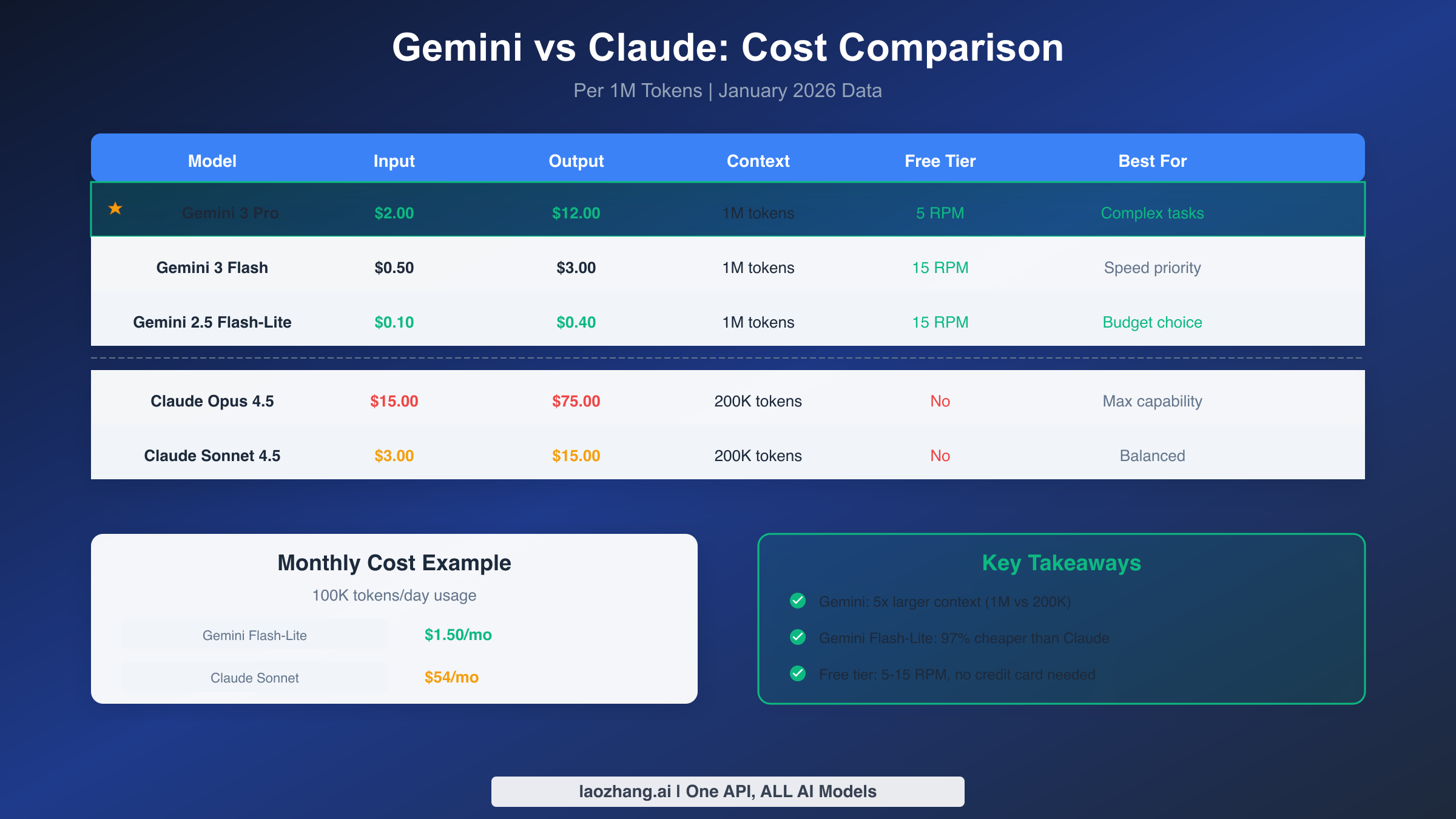
Understanding the exact pricing helps you calculate expected costs for your usage patterns. Gemini 3 Pro Preview, the flagship model, costs $2.00 per million input tokens and $12.00 per million output tokens. This pricing applies to standard usage within 200,000 token contexts, with slightly higher rates for contexts exceeding that threshold. Despite being the most expensive Gemini option, this represents just a fraction of Claude Opus pricing.
Gemini 3 Flash Preview offers substantial savings at $0.50 per million input tokens and $3.00 per million output tokens. For many use cases, Flash quality is indistinguishable from Pro, making it an excellent default choice. The speed advantage further compounds value since faster responses mean you can accomplish more within any given time period.
The budget champion is Gemini 2.5 Flash-Lite at $0.10 input and $0.40 output per million tokens. This model costs 97% less than Claude Sonnet for equivalent token usage. While capability is reduced compared to newer models, Flash-Lite handles basic tasks competently and can serve as your default for routine automation while reserving more capable models for complex work.
For detailed pricing comparisons across all Gemini models and tiers, check our comprehensive Gemini API pricing guide which includes calculators and scenario analysis.
Real-World Cost Scenarios
Let's examine concrete scenarios to illustrate cost differences. Consider a moderate user sending 50 messages daily, with each interaction averaging 1,000 input tokens and 2,000 output tokens. Monthly this totals approximately 1.5 million input tokens and 3 million output tokens.
Using Claude Sonnet at $3.00 input and $15.00 output per million tokens, monthly cost reaches $49.50. The same usage with Gemini 3 Flash costs $6.75, an 86% reduction. Dropping to Gemini Flash-Lite brings monthly costs to just $1.35, enabling heavy usage with negligible expense.
For power users, the savings become even more dramatic. One Hacker News user reported spending over $300 in just two days using Clawdbot with Claude due to inefficient token usage patterns in agent loops. The same usage with Gemini Flash-Lite would cost approximately $15, transforming an unsustainable expense into reasonable operational costs.
Free Tier Optimization
Gemini's free tier provides genuine value for users who optimize their usage patterns. The free tier includes 5 requests per minute for Pro models and up to 15 RPM for Flash variants, with daily limits around 1,000 requests for some models. Importantly, no credit card is required to access the free tier, lowering barriers to experimentation.
Maximizing free tier value requires understanding rate limits and structuring usage accordingly. Batch similar requests together when possible, avoid tight loops that rapidly consume quota, and consider implementing client-side caching for repeated queries. The free tier works best for personal assistants with moderate, spread-out usage rather than burst-heavy automation workflows.
Keep in mind that free tier data may be used (with human review) to improve Google's products, while paid tier usage excludes your data from such use. For sensitive applications, the paid tier provides additional privacy assurances worth the relatively modest cost. For more details on optimizing free tier usage, see our guide on Gemini's free tier limits.
If you're looking for API access without regional restrictions and unified billing across multiple models, platforms like laozhang.ai provide OpenAI-compatible endpoints that aggregate various providers including Gemini, simplifying management for users working with multiple AI services.
Gemini Skills and Advanced Features
Clawdbot's skill system extends its capabilities through modular additions, and several skills specifically leverage Gemini's unique features. Understanding and installing these skills unlocks functionality that isn't possible with text-only models or providers without multimodal support.
Gemini-Specific Skills
The Clawdbot ecosystem includes several skills designed specifically for Gemini integration. The core gemini skill provides CLI access for one-shot queries, summaries, and text generation outside of the main agent loop. This proves useful for quick lookups and scripted automation where you want Gemini responses without engaging the full agent context.
The gemini-computer-use skill enables browser-control agents using Gemini 2.5 and Playwright. This powerful capability allows your assistant to interact with web pages, fill forms, click buttons, and extract information from dynamic content. Computer use scenarios range from automated research to monitoring dashboards and even completing online workflows on your behalf.
For research-heavy workflows, the gemini-deep-research skill connects to Gemini's Deep Research Agent for complex, long-running investigations. This skill orchestrates multiple search and analysis steps to compile comprehensive research reports, handling multi-step reasoning that would require significant manual effort to coordinate.
The gemini-stt skill provides speech-to-text transcription using Gemini's audio processing capabilities. This enables voice message transcription, meeting note generation, and audio content analysis directly within your Clawdbot workflows. The transcription quality rivals dedicated services while integrating seamlessly with your existing assistant setup.
Installing Skills
Skills from ClawdHub, Clawdbot's skill marketplace, install with a simple command. On Linux systems, use clawdhub install skill-slug where skill-slug is the identifier for the desired skill. The macOS Skills UI provides a graphical alternative but isn't available on all configurations.
Custom skills can be developed and placed in your workspace's skills directory or in ~/.clawdbot/skills for personal use across projects. Skills follow a standard structure that Clawdbot automatically discovers and loads, with workspace skills taking precedence over globally installed options.
After installing skills, restart your Clawdbot agent for the changes to take effect. Verify installation by listing available tools with the /tools command in any connected messaging channel. The newly installed skill should appear with its associated capabilities.
Practical Use Cases
Understanding how these skills combine with Gemini's capabilities suggests powerful applications. Consider a research assistant that monitors industry news, transcribes relevant podcasts and videos, and compiles daily briefings. The combination of search, transcription, and summarization skills running on Gemini creates a personalized intelligence service.
For developers, computer use capabilities combined with code understanding enable assistants that can test web applications, document workflows with screenshots, and even help debug by replicating user-reported issues. The multimodal input processing means you can share error screenshots and get analysis without manually transcribing messages.
Content creators benefit from transcription and summarization skills that transform video research into written notes, draft responses to emails based on conversational context, and maintain consistent writing styles across projects. The 1M token context allows including entire project histories for better consistency.
Security Best Practices
Security concerns represent legitimate considerations when running AI assistants with broad system access. Discussions on Hacker News and within the Clawdbot community have highlighted potential risks, and responsible usage requires understanding and mitigating these concerns. Proper configuration significantly reduces attack surface while maintaining functionality.
API Key and Credential Security
The OAuth flow used for Gemini authentication provides inherent security advantages over static API keys. Tokens expire and refresh automatically, limiting the damage if credentials are somehow compromised. However, the stored tokens still warrant protection through proper file permissions and secure system configuration.
Ensure your Clawdbot configuration directory has appropriate permissions with chmod 700 ~/.clawdbot preventing other users on shared systems from reading your credentials. For environment variables containing sensitive information, avoid storing them in shell history or version-controlled files. Consider using a secrets manager for production deployments.
When using API keys instead of OAuth, create keys with minimal required permissions and rotate them periodically. Monitor your API usage dashboards for unexpected activity that might indicate key compromise. Google's Cloud Console provides detailed usage logs and anomaly detection that can alert you to suspicious patterns.
Sandboxing Considerations
Clawdbot's power comes partly from its ability to execute commands and access system resources, but this creates security implications. The project documentation discusses sandbox modes that restrict what actions the agent can take, and production deployments should carefully consider these settings.
For maximum security, run Clawdbot in a container or virtual machine that limits access to sensitive files and systems. Docker provides straightforward isolation, and the project includes configurations for containerized deployment. This approach prevents even compromised agents from accessing host system resources outside the container.
Configure explicit allowlists for file system access, restricting the agent to specific directories rather than broad system access. The working directory configuration in clawdbot.json controls where the agent operates by default, and thoughtful configuration prevents accidental access to sensitive areas.
Prompt Injection Awareness
AI assistants that process external content face prompt injection risks where malicious inputs attempt to manipulate agent behavior. While no complete solution exists, understanding the risk informs defensive practices.
Avoid having your assistant automatically process untrusted content without review. When using Clawdbot to analyze emails, web pages, or user-submitted content, be aware that malicious actors might embed instructions attempting to exfiltrate data or change assistant behavior. The Gemini team continues improving model robustness, but defense-in-depth remains prudent.
Consider implementing the community-developed Chord project as an additional security layer. Chord analyzes commands before execution using a separate model, blocking potentially risky operations. While this adds overhead and token costs, it provides another checkpoint for sensitive deployments.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even well-configured systems occasionally encounter problems. This section addresses the most common issues users face with Gemini integration and provides diagnostic steps to resolve them quickly.
Authentication Failures
If authentication fails during the OAuth flow, first verify your internet connection and ensure Google's servers are accessible. Corporate networks sometimes block OAuth endpoints, requiring VPN or network configuration changes. Try accessing accounts.google.com in a browser to confirm basic connectivity.
For headless server authentication, ensure you're properly transferring the verification URL to a device with a browser. The URL is single-use and expires, so complete the flow promptly after generating it. If the URL expires, simply restart the authentication process.
Token refresh failures after successful initial authentication often indicate system clock synchronization issues. OAuth tokens use time-based validation, and clock drift exceeding a few minutes causes rejection. Synchronize your system clock with NTP servers using ntpdate or your platform's time sync service.
Rate Limit Errors
Exceeding Gemini's rate limits produces errors that might seem like authentication failures. The free tier limits requests to 5-15 per minute depending on model, and burst usage quickly exhausts this quota. Implement exponential backoff in automated workflows and consider upgrading to paid tier for production use.
Check your current quota status in Google AI Studio, which provides dashboards showing usage and remaining limits. If you're hitting limits unexpectedly, review your agent configuration for loops or retry logic that might generate excessive requests.
Model Switching Issues
If the /model command doesn't seem to change your active model, verify the shortcut or full model name is correct. Typos produce silent failures with the previous model remaining active. The command clawdbot models list shows available models and confirms the current selection. Configuration file settings override session changes, so edits to clawdbot.json affect future sessions but not the current one. Restart the agent after configuration changes for them to take effect.
Diagnostic Commands
Clawdbot includes several diagnostic tools for troubleshooting. The command clawdbot status provides a snapshot of local configuration and running processes. For provider-specific issues, clawdbot models status shows authentication state and current model selection.
The comprehensive diagnostic clawdbot doctor validates configuration, checks for common issues, and can repair certain problems automatically. Run this command when encountering unexpected behavior before diving into manual troubleshooting.
For real-time debugging, clawdbot logs --follow streams the event log, showing requests, responses, and errors as they occur. This visibility helps identify where problems occur in the processing pipeline and whether issues stem from configuration, authentication, or the Gemini API itself.
Conclusion
Integrating Google Gemini with Clawdbot opens possibilities for cost-effective, powerful AI assistants that were previously impractical for personal use. The generous free tier, 1 million token context window, and multimodal capabilities make Gemini an excellent choice for users seeking alternatives to Claude's pricing structure.
Getting started requires just two commands to enable authentication, with the broader ecosystem of skills and configuration options available for customization as your needs evolve. The cost savings can be dramatic, with Gemini Flash-Lite costing 97% less than Claude Sonnet for equivalent usage while still providing capable AI assistance for routine tasks.
Security considerations deserve attention proportional to your use case sensitivity. Personal assistants with limited system access carry minimal risk, while production deployments processing sensitive data warrant containerization and careful permission configuration. The community continues developing additional security tools and best practices.
The Clawdbot project's rapid growth suggests vibrant ongoing development, and Gemini integration will likely improve as both platforms evolve. Joining the Discord community provides access to latest developments, troubleshooting help, and inspiration for creative applications. Whether you're automating personal workflows, building a family assistant, or exploring agentic AI capabilities, the Clawdbot and Gemini combination provides a solid, economical foundation.