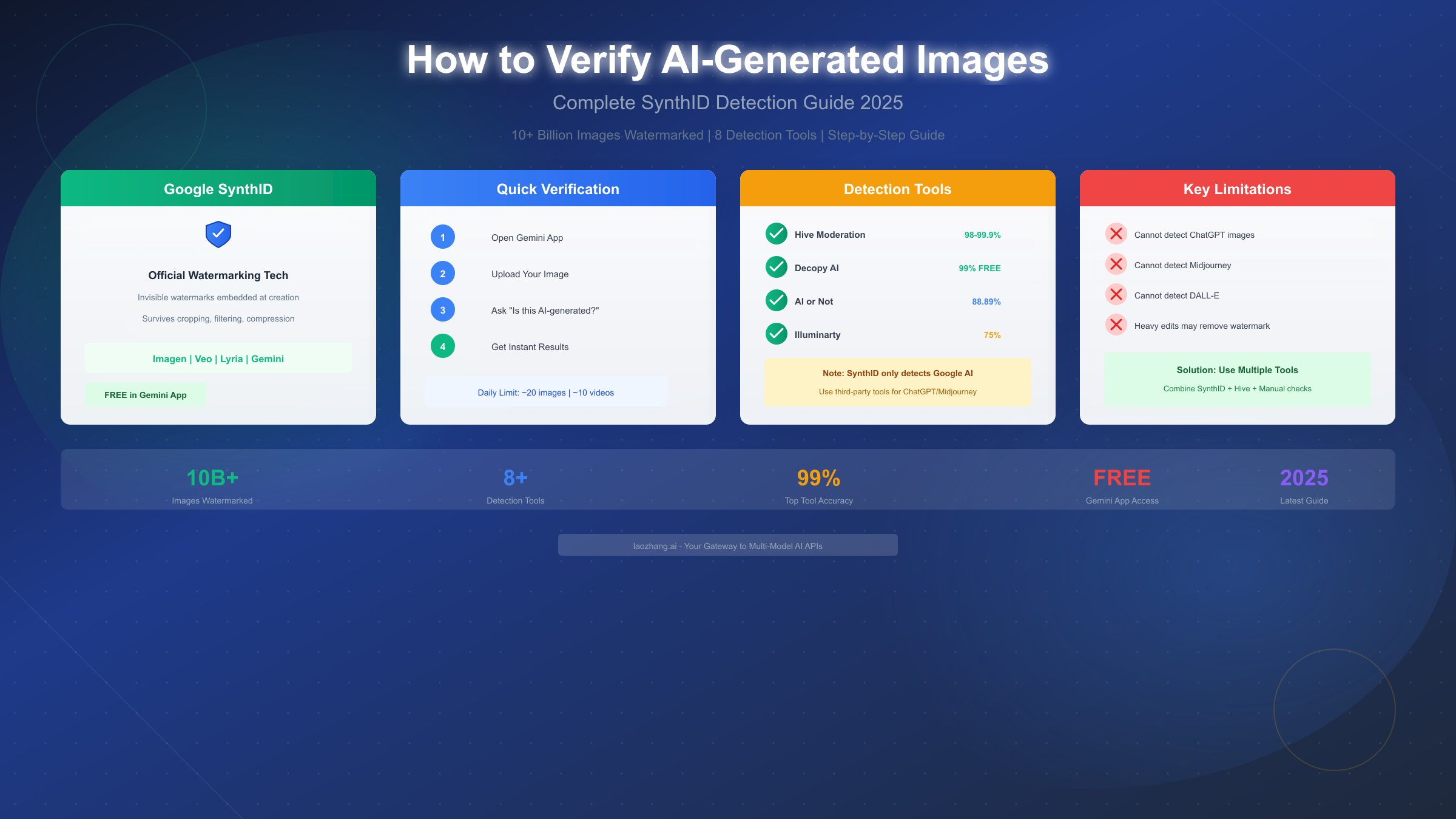
Google's SynthID technology allows you to verify if an image was created with Google AI through the Gemini app in seconds. Simply upload any image to Gemini and ask "Was this created with Google AI?" - the app will check for invisible SynthID watermarks and return results immediately. As of December 2025, over 10 billion pieces of content have been watermarked with SynthID, covering images from Imagen, videos from Veo, and audio from Lyria models. However, there's a critical limitation: SynthID only detects Google-generated content, meaning it won't identify images from ChatGPT, Midjourney, or DALL-E.
This comprehensive guide covers everything you need to know about verifying AI-generated images, from Google's official SynthID detection to third-party tools that can identify content from any AI source. Whether you're a fact-checker, journalist, content creator, or concerned citizen, you'll learn exactly how to distinguish real photographs from AI-generated imagery.
What is SynthID and How Does It Work?
SynthID represents Google DeepMind's groundbreaking approach to AI content authentication. Rather than relying on visible watermarks that can be easily removed, SynthID embeds imperceptible digital signatures directly into AI-generated content at the moment of creation. This technology has fundamentally changed how we can verify the origin of digital media in an age where AI-generated content has become increasingly sophisticated and difficult to distinguish from authentic material.
The core technology behind SynthID uses two neural networks working in tandem. The first network modifies individual pixel values in images so subtly that the human eye cannot perceive any difference from the original. These modifications are strategically selected to ensure the watermark remains detectable even after the image undergoes common transformations like cropping, compression, filtering, rotation, or even being captured via screenshot. The second neural network then analyzes images to detect these invisible signatures, providing confidence levels about whether content originated from Google's AI systems.
What makes SynthID particularly powerful is its resilience to manipulation. According to Google DeepMind's official documentation (https://deepmind.google/models/synthid/ ), the watermarking system has been trained on diverse datasets to maintain detection accuracy across a wide range of real-world scenarios. When you compress an image for web upload, apply Instagram filters, or convert between file formats, the SynthID watermark typically survives these transformations intact. This robustness addresses a fundamental challenge in digital authentication - creating markers that persist through the natural lifecycle of online content.
The scope of SynthID's deployment has expanded significantly since its initial launch. Originally focused solely on images generated by Google's Imagen model, SynthID now covers multiple content modalities. Video content from Veo, Google's video generation model, carries SynthID watermarks embedded into video frames. Audio generated by Lyria includes inaudible watermarks that persist even through noise addition, MP3 compression, and speed adjustments. Even text output from Gemini can be watermarked using SynthID Text, which subtly adjusts the probability scores assigned to word tokens during generation.
The scale of SynthID's deployment underscores its importance in the AI ecosystem. Google reports that over 10 billion pieces of content have been watermarked with SynthID technology, making it one of the most widely deployed AI authentication systems in existence. This massive deployment means that a significant portion of AI-generated content circulating online - at least that originating from Google's systems - can potentially be identified and verified.
Understanding how SynthID detection reports results is crucial for proper interpretation. When you submit an image for verification, the system doesn't simply return a binary "AI" or "not AI" answer. Instead, it provides confidence levels that indicate the likelihood of SynthID watermark presence. A strong positive detection means the system is highly confident the image was generated by Google AI. A partial or uncertain detection might indicate the image was generated by Google AI but has been significantly modified, or that the analysis is inconclusive. A negative result means no SynthID watermark was found - but this doesn't necessarily mean the image isn't AI-generated, only that it wasn't created using Google's watermarked systems.
Step-by-Step: Verify Images with Google Gemini App
The most accessible way to verify if an image was created with Google AI is through the Gemini app, which provides a user-friendly interface for SynthID detection. This method requires no technical knowledge and works on both mobile devices and desktop browsers, making it suitable for everyday users who want to quickly check suspicious images.
Before you begin, ensure you have the necessary prerequisites. You'll need the Gemini app installed on your device (available on iOS from the App Store and Android from Google Play) or access to the Gemini web interface at gemini.google.com. A Google account is required to use the verification feature. Make sure your app is updated to the latest version, as the AI verification feature was introduced in November 2025 and may not be available in older versions.
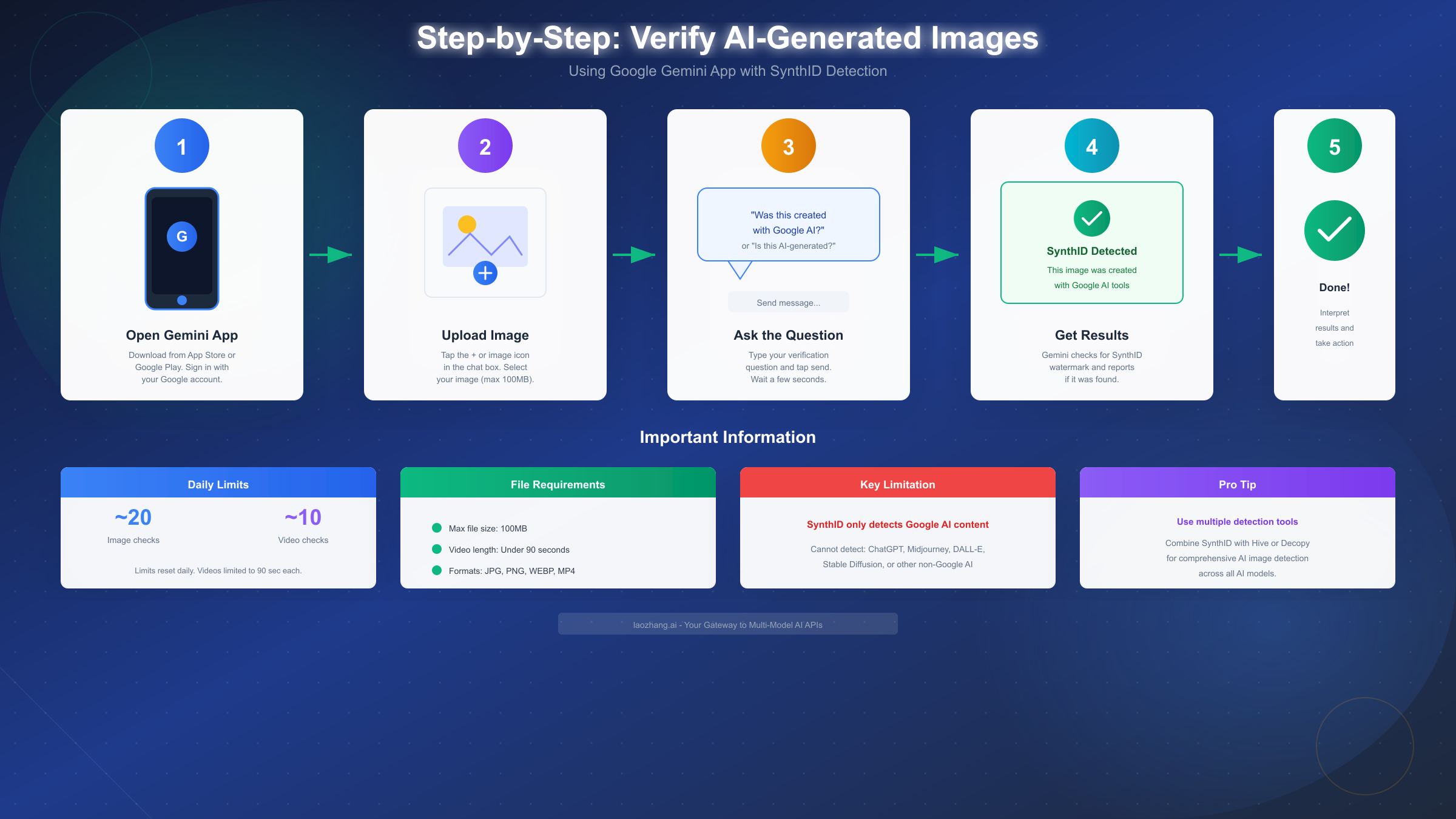
Step 1: Open the Gemini application and navigate to a new conversation. Launch the app on your mobile device or open the web interface in your browser. If you're not already signed in, authenticate with your Google account. Start a fresh conversation to keep your verification queries organized and easy to reference later.
Step 2: Upload the image you want to verify. Look for the "+" icon or image icon in the chat input area. Tap this to access your device's photo gallery or file system. Select the image you want to check. The image file must be under 100MB in size - if your file exceeds this limit, you'll need to compress it first. Supported formats include JPG, PNG, WEBP, and other common image formats.
Step 3: Ask Gemini to verify the image. Once your image is uploaded and visible in the chat, type a verification question. Effective questions include:
- "Was this image created with Google AI?"
- "Is this AI-generated?"
- "Check if this has a SynthID watermark"
- "Can you verify if this was made with Imagen?"
Tap send and wait a few seconds for Gemini to analyze the image.
Step 4: Interpret the verification results. Gemini will respond with information about whether a SynthID watermark was detected. If a watermark is found, the response will confirm that the image was created or edited using Google AI tools. If no watermark is detected, Gemini will indicate this - but remember, this doesn't prove the image is real, only that it wasn't created with Google's watermarked systems.
Step 5: Understand and act on the results. A positive SynthID detection provides strong evidence of Google AI origin. However, a negative result requires additional investigation using other tools if you suspect the image might be AI-generated from non-Google sources like ChatGPT's DALL-E, Midjourney, or Stable Diffusion.
Important usage limits apply to the verification feature. Google implements daily quotas to manage system resources. As of December 2025, users can perform approximately 20 image verification checks and 10 video verification checks per day. Video files must be under 90 seconds in length individually, with a total daily limit of 5 minutes of video content. If you reach these limits, the Gemini app will notify you, and you'll need to wait until the next day for your quota to reset.
Troubleshooting common issues can save time and frustration. If verification fails, first check your internet connection - the feature requires server-side processing. Ensure your image file isn't corrupted by opening it in another application first. If the app reports an error, try resizing the image to a smaller resolution or converting to a different format. Some heavily compressed images or images that have been significantly edited may produce inconclusive results.
Complete AI Image Detection Tools Comparison
While SynthID provides excellent detection for Google AI content, a comprehensive verification strategy requires access to multiple tools. The AI image detection landscape includes several powerful options, each with distinct strengths and limitations. Understanding these tools allows you to choose the right solution for your specific needs.
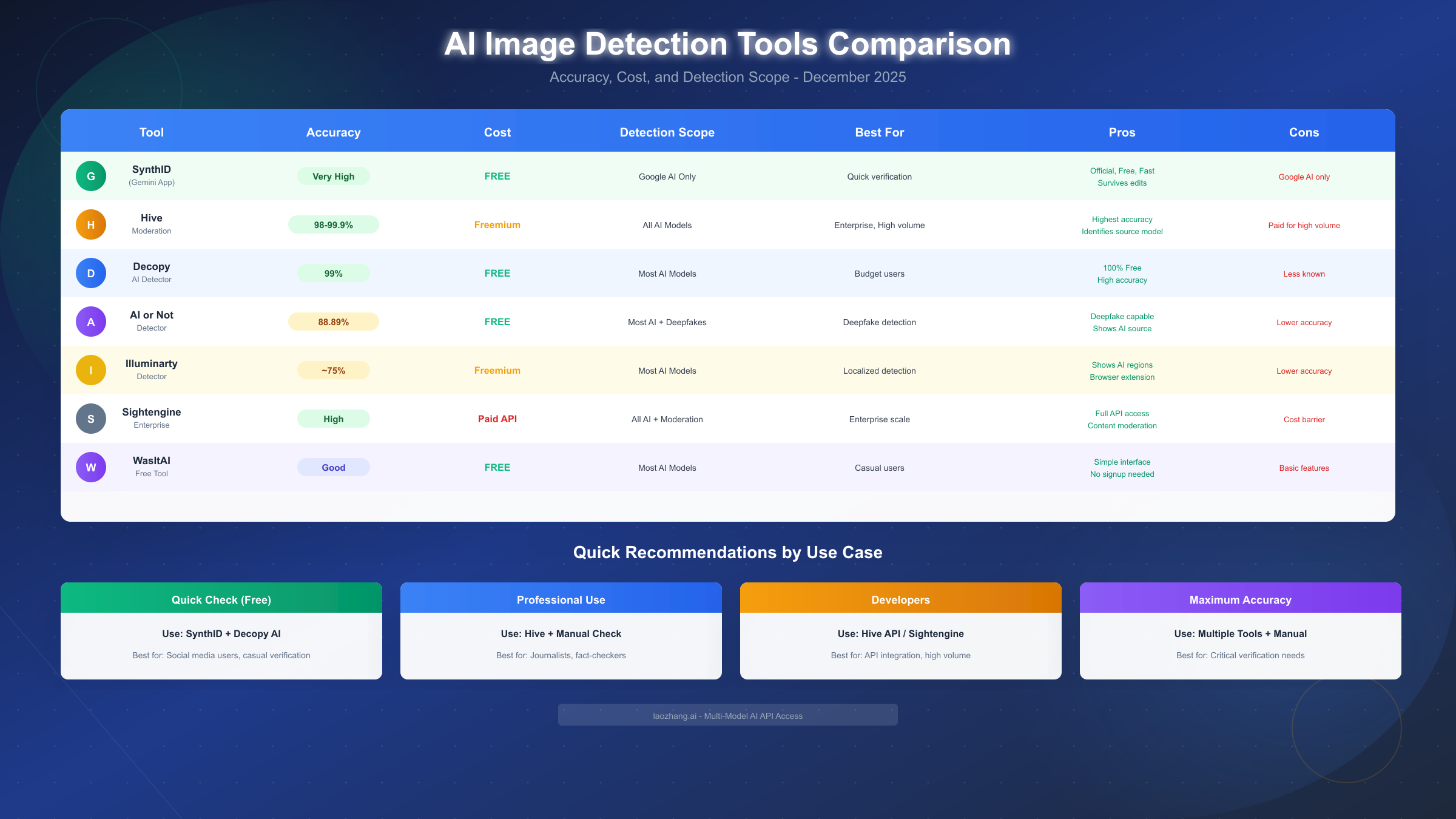
Google SynthID (via Gemini) leads in detecting Google-generated content with very high accuracy. As an official first-party solution, it provides authoritative results for content from Imagen, Veo, Lyria, and Gemini models. The major limitation is its narrow scope - it cannot detect AI content from any non-Google source. Best suited for quick verification of suspected Google AI content, it's completely free to use within daily limits.
Hive Moderation stands out for its exceptional accuracy and broad detection capabilities. Independent testing shows accuracy rates between 98% and 99.9% for identifying AI-generated images across multiple AI models. Unlike SynthID, Hive can detect content from virtually any AI image generator including Midjourney, DALL-E, Stable Diffusion, and others. The platform also identifies the specific AI model used to create an image, providing valuable forensic information. Hive offers a freemium model with limited free checks, while enterprise users pay for higher volumes. This makes it the top choice for professional fact-checkers and journalists who need reliable, comprehensive AI detection.
Decopy AI Detector offers a compelling combination of high accuracy and zero cost. Claiming 99% accuracy based on training with a 3-million-image dataset, Decopy provides detection capabilities across most major AI models. The platform's completely free access model makes it an excellent option for budget-conscious users or those with high-volume verification needs. While less established than Hive, real-world testing suggests reliable performance for most common AI generators.
AI or Not specializes in deepfake detection alongside general AI image identification. With approximately 88.89% accuracy for deepfake content, this tool fills an important niche for verifying manipulated photographs of real people. The platform recognizes content from Midjourney, Stable Diffusion, DALL-E, and other popular generators, and importantly, it identifies which specific AI system created the image. This source identification capability proves valuable when investigating the origin of suspicious content.
Illuminarty differentiates itself through localized detection capabilities. Rather than simply classifying an entire image as AI or human-created, Illuminarty can pinpoint exactly which regions of an image contain AI-generated content. This feature proves particularly valuable for detecting images where AI has been used to edit or composite elements into authentic photographs. The platform achieves approximately 75% overall accuracy and offers a convenient browser extension for real-time detection while browsing. The freemium model provides basic access with paid tiers for advanced features.
Sightengine targets enterprise deployments with comprehensive content moderation features. Beyond AI detection, the platform offers full content moderation capabilities including detection of inappropriate content, text recognition, and more. API-based access enables integration into existing workflows and applications, making it suitable for platforms and publishers who need to scan high volumes of user-generated content. The paid API model means it's not suitable for individual users, but provides excellent value for enterprise-scale operations.
WasItAI provides simple, accessible detection for casual users. The platform's straightforward interface requires no signup or account creation - simply upload an image and receive results. While detailed accuracy statistics aren't published, the tool provides reasonable detection across most common AI generators. This simplicity makes it ideal for quick checks when sophisticated analysis isn't required.
For comprehensive verification of potentially AI-generated images, consider using multiple tools in combination. Start with SynthID via Gemini for Google AI detection, then verify against Hive or Decopy for non-Google sources. This multi-tool approach significantly reduces the chance of missing AI-generated content regardless of its source.
How to Detect Non-Google AI Images
Understanding SynthID's limitations is essential for effective AI image verification. While Google's technology excels at detecting its own AI-generated content, the majority of AI images circulating online come from other sources. ChatGPT's DALL-E integration, Midjourney's distinctive artistic styles, Stable Diffusion's open-source variations, and numerous other tools generate vast quantities of synthetic imagery that SynthID simply cannot identify.
The technical reason for this limitation is straightforward. SynthID watermarks are embedded during the image generation process by Google's systems. Images created by OpenAI, Midjourney, Stability AI, or other providers never pass through Google's watermarking infrastructure, so they contain no SynthID signatures to detect. This isn't a flaw in SynthID - it's an inherent limitation of any watermarking approach. Only content that passes through the watermarking system can be detected by that system.
Third-party detection tools bridge this gap using different technical approaches. Rather than looking for specific watermarks, tools like Hive Moderation and Decopy AI analyze the statistical properties of images to identify patterns characteristic of AI generation. Machine learning models trained on millions of AI and human-created images learn to recognize subtle artifacts, texture patterns, and other signatures that distinguish synthetic content. This approach enables detection across any AI generator, though typically with lower confidence than watermark-based verification.
Hive Moderation provides the most reliable non-Google AI detection. To use Hive for verification, visit hivemoderation.com and navigate to their AI detection tool. Upload your image through their web interface and wait for analysis. Hive will return a confidence score indicating the likelihood of AI generation, along with an identification of the probable source model when possible. For images from ChatGPT, Midjourney, or Stable Diffusion, Hive typically provides accurate source attribution alongside detection results.
Decopy AI offers a free alternative with similar capabilities. Access the platform at decopy.ai and use their image analysis tool. Upload suspicious images to receive AI probability scores and potential source identification. While the interface is simpler than Hive's enterprise platform, the underlying detection capabilities remain strong for most use cases.
Manual artifact detection provides a valuable complement to automated tools. AI image generators, despite their sophistication, still produce characteristic artifacts that trained observers can identify. Text within AI images often contains subtle errors - letters that don't quite form correctly, words that become garbled, or fonts that shift inconsistently. Human hands remain a weakness for most generators, frequently appearing with too many or too few fingers, unusual poses, or inconsistent anatomy. Shadows and lighting often lack physical consistency, with light sources implied by shadows that don't match the apparent illumination of subjects. Background elements may contain repetitive patterns or impossible geometric relationships that reveal synthetic origin.
Examining image metadata provides another verification avenue. Authentic photographs typically contain EXIF data recording camera model, settings, date, and sometimes GPS coordinates. While this metadata is easily stripped or faked, its complete absence from an image claiming to be a photograph warrants suspicion. Some AI generators include identifying information in file metadata, though this is inconsistent.
C2PA standards represent an emerging approach to content authenticity. The Coalition for Content Provenance and Authenticity (C2PA) defines standards for cryptographically signing content at creation and tracking its edit history. Google has begun rolling out C2PA support, enabling verification of not just Google AI content but any content from C2PA-participating platforms. As adoption increases, checking for C2PA credentials will become an increasingly valuable verification step.
Understanding SynthID Detection Limitations
Honest assessment of SynthID's limitations ensures appropriate expectations and prevents false confidence in verification results. While SynthID represents significant progress in AI content authentication, it operates within meaningful constraints that affect its practical utility.
The most fundamental limitation is SynthID's scope - it only detects Google AI content. Images from ChatGPT's DALL-E, Midjourney, Stable Diffusion, Adobe Firefly, and numerous other generators contain no SynthID watermarks and will never be detected regardless of how obviously synthetic they appear. This means that for the vast majority of AI images encountered online, SynthID provides no useful information. A negative SynthID result should never be interpreted as evidence that an image is authentic.
Heavy modifications can degrade or remove SynthID watermarks entirely. While the system is designed to survive common transformations like compression and cropping, extreme manipulations can remove detectable signatures. Significant resolution changes, aggressive filters, color space conversions, or combinations of multiple edits may reduce watermark detectability below useful thresholds. Images that have been printed and rescanned, or captured from screens, may lose their watermarks entirely.
Text watermarking faces particular challenges with rewriting and translation. SynthID Text works by subtly influencing word choice during generation. When AI-generated text is paraphrased, summarized, or translated, these statistical patterns are destroyed. A passage originally generated by Gemini, once run through a different AI for "humanization" or translated into another language, becomes effectively undetectable.
No industry-wide watermarking standard exists. Google has SynthID, but Microsoft, Meta, OpenAI, and other major AI providers use different proprietary systems - or no watermarking at all. This fragmented landscape means comprehensive AI detection cannot rely on any single watermarking technology. Achieving reliable detection across the full AI ecosystem requires combining multiple approaches.
Adversarial techniques can intentionally defeat watermarking. Research from the University of Maryland and other institutions has demonstrated methods to remove or mask AI watermarks while preserving image quality. While SynthID incorporates robustness against casual manipulation, determined adversaries with technical knowledge can potentially defeat the system. This limitation is particularly relevant for high-stakes verification scenarios involving motivated bad actors.
Detection accuracy metrics for non-text modalities remain unpublished. While Google provides some information about SynthID Text performance, detailed accuracy statistics for image and video watermark detection haven't been publicly released. This makes it difficult to quantify false positive and false negative rates or understand performance across different content types.
Despite these limitations, SynthID provides valuable verification capabilities when applied appropriately. For suspected Google AI content, it offers reliable authentication. Combined with third-party detection tools and manual analysis, it contributes to a comprehensive verification workflow. The key is understanding what SynthID can and cannot tell you, and supplementing accordingly.
Which Detection Tool Should You Use?
Selecting the right AI detection approach depends on your specific use case, the types of content you typically verify, and your resource constraints. Different users have different needs, and the optimal tool or combination of tools varies accordingly.
For casual social media users who encounter suspicious images occasionally, the Gemini app provides the most accessible starting point. Its free access, simple interface, and authoritative results for Google AI make it ideal for quick verification without technical complexity. When Gemini returns negative results, supplementing with Decopy AI's free verification covers non-Google sources without cost. This combination addresses most verification needs for everyday users while requiring no financial investment or technical expertise.
Journalists and fact-checkers require higher confidence and broader coverage. Professional verification workflows should employ Hive Moderation as a primary tool due to its industry-leading accuracy and comprehensive source detection. Supplementing Hive results with manual artifact analysis provides additional confidence. For critical stories, consulting multiple detection tools and documenting their agreement helps establish credibility. Consider the ChatGPT image generation capabilities when investigating potentially synthetic images, as understanding how AI generates content improves detection intuition.
Content moderators and platform operators need scalable, automated solutions. Sightengine's API-based approach enables integration into content pipelines for automated scanning at scale. Hive also offers API access for enterprise deployments. The investment in paid services is justified by the volume of content requiring verification and the risks associated with synthetic content reaching audiences. These platforms should also implement C2PA verification as adoption of that standard grows.
Developers building verification features benefit from understanding the full landscape of available APIs. For those needing access to multiple AI models and services including detection capabilities, services like laozhang.ai provide aggregated API access that simplifies integration. This is particularly valuable for applications targeting international users who may face regional restrictions on direct API access.
When maximum accuracy is essential, employ a multi-layered verification approach. Start with SynthID via Gemini for Google AI detection. Continue with Hive Moderation for comprehensive AI coverage. Supplement with manual artifact analysis focusing on text, hands, and lighting. Check image metadata for authenticity indicators. Verify against C2PA credentials if available. Document findings from each verification step. This comprehensive approach minimizes false negatives while building a robust evidence base.
A decision flowchart simplifies tool selection: First, ask whether you need to verify Google AI specifically - if yes, use Gemini. If the image might be from any AI source, proceed to Hive or Decopy. For deepfake concerns specifically, add AI or Not to your workflow. For professional or high-stakes verification, use all available tools and document results. For casual checks, Gemini plus Decopy provides free, reasonable coverage.
API Access and Developer Options
Developers integrating AI detection into applications have several API options available, each suited to different requirements and use cases. Understanding these options enables building effective verification features while managing costs and complexity.
Google Cloud Vision API provides official access to Google's content analysis capabilities. The SafeSearch detection feature can identify potentially problematic content, though it's important to note this isn't the same as SynthID detection - SafeSearch focuses on content moderation rather than AI origin verification. Developers seeking programmatic SynthID access should monitor Google's announcements, as API access to SynthID detection specifically may be released in the future. For comprehensive Gemini API capabilities including image analysis, Google's documentation provides detailed integration guidance.
Hive Moderation API offers the most comprehensive AI detection capabilities for developers. The API enables automated verification of images against Hive's detection models, returning confidence scores and source identification. Pricing operates on a per-request basis with volume discounts for enterprise customers. Integration requires obtaining API credentials and implementing RESTful calls - Hive provides SDKs and documentation to streamline development.
Sightengine API combines AI detection with broader content moderation features. Developers building platforms that need both AI verification and content safety analysis benefit from Sightengine's unified approach. The API returns structured responses enabling automated processing and flagging. Pricing scales with usage, making it cost-effective for platforms with varying verification volumes.
For applications serving users in regions with access restrictions, API gateway services provide valuable connectivity. Services like laozhang.ai aggregate access to multiple AI models and tools through unified APIs, simplifying integration while solving geographic access challenges. This approach is particularly relevant for developers building international applications where users may face restrictions accessing Google services directly. For comprehensive API documentation and multi-model access capabilities, refer to the official documentation at docs.laozhang.ai.
Implementation considerations for developers include caching detection results to minimize API costs for repeated verification of the same content. Rate limiting prevents accidental cost overruns from excessive requests. Error handling should account for API unavailability and implement fallback behaviors. Privacy considerations require careful handling of user-uploaded images - ensure compliance with applicable regulations regarding image processing and storage.
Basic implementation pattern for AI image detection follows a standard workflow: accept image upload from user, validate file format and size, submit to detection API, parse response for confidence scores, present results to user with appropriate context. Most detection APIs support both direct image upload and URL-based submission, enabling flexibility in implementation architecture.
Summary and Quick Reference Guide
Verifying AI-generated images requires understanding both the capabilities and limitations of available tools. This guide has covered the full landscape from Google's SynthID technology to third-party detection services, providing the knowledge needed for effective verification regardless of the AI source.
Key takeaways for effective AI image verification:
The Gemini app provides free, accessible SynthID detection for Google AI content. Simply upload an image and ask if it was created with Google AI to receive verification results. Daily limits of approximately 20 image checks apply.
SynthID only detects Google AI content - images from ChatGPT, Midjourney, DALL-E, and other sources require different tools. Never interpret a negative SynthID result as proof an image is authentic.
For comprehensive detection across all AI sources, Hive Moderation offers 98-99.9% accuracy with source identification. Decopy AI provides a free alternative with claimed 99% accuracy.
Multiple detection tools used together provide the highest confidence. Combine SynthID, Hive or Decopy, and manual artifact analysis for critical verifications.
Manual artifact detection focuses on text errors, hand anomalies, lighting inconsistencies, and background irregularities - common weaknesses in current AI generators.
API access enables integration of detection capabilities into applications. Hive and Sightengine offer comprehensive APIs, while services like laozhang.ai provide aggregated access for international developers.
Quick reference by use case:
| Scenario | Recommended Approach |
|---|---|
| Quick check for Google AI | Gemini app - free, fast, official |
| Comprehensive verification | Hive + Gemini + manual analysis |
| Free budget option | Decopy AI + Gemini |
| High-volume platform needs | Sightengine API or Hive API |
| Deepfake detection | AI or Not + Hive |
| Developer integration | Hive API + laozhang.ai for international access |
Looking ahead, AI detection technology continues evolving alongside AI generation capabilities. C2PA standards for content provenance are gaining adoption, promising improved verification through cryptographic attestation. Google continues expanding SynthID across content types. Third-party detectors continually update their models to keep pace with new AI generators.
The most effective approach combines multiple verification methods, maintains awareness of each tool's limitations, and applies appropriate skepticism to all results. No single tool provides perfect detection, but thoughtful combination of available resources enables confident verification for most scenarios.
For ongoing updates on AI detection capabilities, API access options, and the latest tools, explore related guides on AI video models and Gemini API pricing to stay current with the rapidly evolving AI landscape.