If you've searched for "how to fine-tune Gemini 3" and found confusing or outdated information, you're not alone. Google's AI landscape has evolved rapidly in 2025, and the fine-tuning options can be overwhelming. This guide cuts through the confusion and gives you everything you need to create a custom Google AI model—whether you have a cloud budget or prefer free local options.
The short answer: Gemini 3 fine-tuning is not publicly available as of December 2025. But don't close this tab—you have excellent alternatives. Gemini 2.5 models can be fine-tuned on Google's Vertex AI platform, and Google's open-source Gemma 3 models can be fine-tuned for free on Google Colab. This guide covers both paths in detail, complete with working code you can use today.
Can You Fine-Tune Gemini 3? The Current Reality
Let's address the elephant in the room: Gemini 3 was released on November 18, 2025, and it's Google's most capable model to date. You can use it for inference across Google AI Studio, the Gemini app, and Vertex AI. However, supervised fine-tuning for Gemini 3 is currently limited to enterprise customers through Vertex AI.
For developers and smaller organizations, the official Google AI for Developers documentation states: "With the deprecation of Gemini 1.5 Flash-001 in May 2025, we no longer have a model available which supports fine-tuning in the Gemini API." Google has indicated they plan to bring fine-tuning support back to the public Gemini API, but no timeline has been announced.
What does this mean for you? If you need to fine-tune a Google AI model today, you have two practical options: use Gemini 2.5 models through Vertex AI (paid, cloud-based), or use Gemma 3 models locally or on free Google Colab (free, open-source). The good news is that both options are fully capable of creating high-quality custom models for your specific use cases.
Why fine-tune at all? Supervised fine-tuning teaches a model to perform specific tasks better than the base model can with prompting alone. According to Google's documentation, fine-tuning is most effective for domain expertise (legal, medical, finance), format customization, task-specific optimization, and behavior control. If you've tried prompt engineering and aren't getting consistent results, fine-tuning may be your solution.
All Google AI Fine-Tuning Options Compared
Understanding your options is the first step to choosing the right path. Here's how the three main approaches compare as of December 2025:

Gemini 3 represents Google's frontier model, but its fine-tuning capabilities are restricted to enterprise customers with existing Google Cloud contracts. If you're a large organization already using Vertex AI, you may have access through your enterprise agreement. For everyone else, Gemini 3 fine-tuning isn't currently an option.
Gemini 2.5 on Vertex AI is the production-ready choice for businesses and developers with a Google Cloud budget. The Vertex AI documentation (updated December 14, 2025) confirms that gemini-2.5-pro, gemini-2.5-flash, and gemini-2.5-flash-lite all support supervised fine-tuning. You get managed infrastructure, automatic scaling, and enterprise-grade security. The trade-off is cost—you pay for training tokens and inference.
Gemma 3 is Google's open-source model family, released in March 2025 with the same architecture as Gemini 2.0. Available in 1B, 4B, 12B, and 27B parameter sizes, Gemma 3 can be fine-tuned on your own hardware or for free on Google Colab using tools like Unsloth. According to Unsloth's documentation, their framework makes Gemma 3 fine-tuning 1.6x faster with 60% less VRAM, enabling the 4B model to run on free Colab T4 GPUs.
The key differences come down to cost, control, and capability. Vertex AI offers the most powerful models with zero infrastructure management but requires a cloud budget. Gemma 3 gives you complete control and costs nothing to train, but you're responsible for deployment. For most developers starting out, Gemma 3 is the recommended starting point—you can learn the process for free and scale to Vertex AI when you need production capabilities.
Which Method Should You Choose? Decision Framework
Choosing between fine-tuning approaches depends on your specific situation. Use this decision framework to find your path:
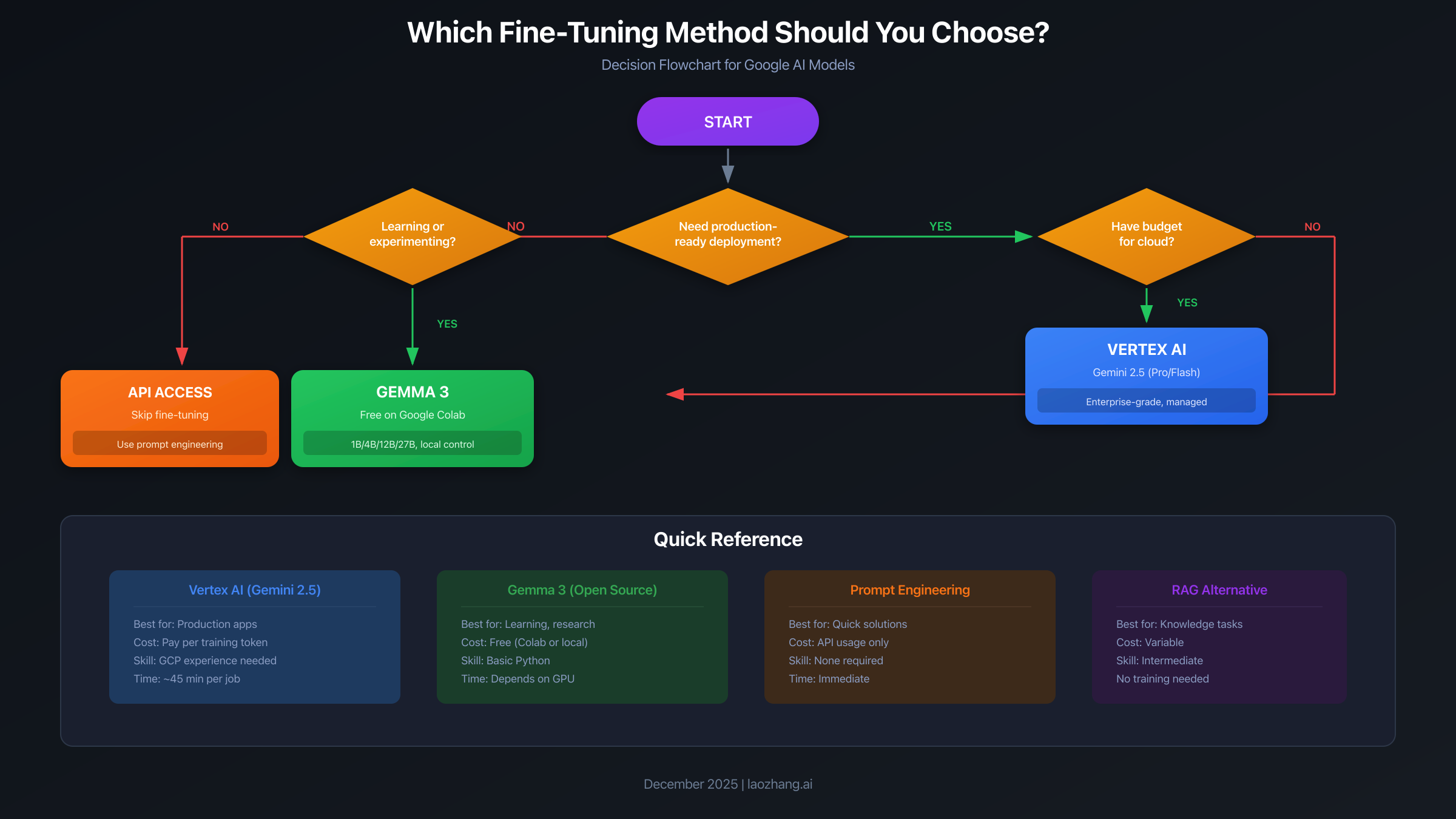
Choose Vertex AI (Gemini 2.5) if:
- You need production-ready deployment with SLA guarantees
- Your organization already has a Google Cloud account
- You have budget for cloud training and inference
- You require enterprise security features (VPC, IAM, audit logs)
- Your use case demands the highest model quality
Choose Gemma 3 (Free/Local) if:
- You're learning fine-tuning for the first time
- Budget is a primary constraint
- You want full control over your model weights
- Privacy concerns require keeping data on-premises
- You're building a prototype before investing in cloud infrastructure
Consider skipping fine-tuning entirely if:
- Your task can be solved with good prompt engineering
- You only need retrieval-augmented generation (RAG)
- Your data changes frequently (fine-tuning bakes in knowledge)
- You have fewer than 50-100 quality training examples
One important consideration: these approaches aren't mutually exclusive. Many teams start with Gemma 3 to validate their approach and training data, then move to Vertex AI for production deployment. The data format (JSONL with user/model pairs) is compatible across both platforms, making migration straightforward.
If you decide that fine-tuning isn't right for your use case, services like laozhang.ai provide unified API access to multiple AI models, allowing you to use different providers based on your needs without managing separate integrations. Sometimes the right solution is better prompting with a capable base model rather than fine-tuning.
Fine-Tune Gemini 2.5 on Vertex AI (Step-by-Step)
This section walks you through fine-tuning Gemini 2.5 Flash on Google Cloud's Vertex AI platform. This is the production-ready path with managed infrastructure and enterprise features.
Prerequisites: You'll need a Google Cloud account with billing enabled, the gcloud CLI installed, and Python 3.9+. If you're new to Google Cloud, you can get $300 in free credits for new accounts.
Step 1: Project Setup. Start by enabling the required APIs and creating a storage bucket for your training data. Run these commands in your terminal:
bashexport PROJECT_ID="your-project-id" export REGION="us-central1" export BUCKET_NAME="your-bucket-name" # Enable required APIs gcloud services enable aiplatform.googleapis.com storage.googleapis.com # Create a Cloud Storage bucket gsutil mb -l $REGION gs://$BUCKET_NAME
Step 2: Prepare Training Data. Vertex AI requires data in JSONL format where each line contains a conversation with user and model messages. According to Google's data preparation guide, you should start with at least 100 examples for best results.
Here's the required format:
json{"contents": [{"role": "user", "parts": [{"text": "Summarize this article about climate change..."}]}, {"role": "model", "parts": [{"text": "The article discusses three main points..."}]}]} {"contents": [{"role": "user", "parts": [{"text": "Write a product description for..."}]}, {"role": "model", "parts": [{"text": "Introducing the revolutionary..."}]}]}
Create your training file locally, then upload to Cloud Storage:
bashgsutil cp train.jsonl gs://$BUCKET_NAME/data/train.jsonl gsutil cp validation.jsonl gs://$BUCKET_NAME/data/validation.jsonl
Step 3: Launch the Fine-Tuning Job. Install the Vertex AI SDK and create your training script:
pythonimport vertexai from vertexai.tuning import sft # Initialize Vertex AI vertexai.init(project="your-project-id", location="us-central1") # Configure and start the fine-tuning job sft_tuning_job = sft.train( source_model="gemini-2.5-flash", train_dataset="gs://your-bucket/data/train.jsonl", validation_dataset="gs://your-bucket/data/validation.jsonl", epochs=4, adapter_size=4, # Options: 1, 2, 4, 8 learning_rate_multiplier=1.0, tuned_model_display_name="my-custom-gemini-model" ) # Monitor progress print(f"Job started: {sft_tuning_job.resource_name}")
The training job typically takes 30-60 minutes depending on your dataset size. You can monitor progress in the Vertex AI console or by polling the job status programmatically.
Step 4: Use Your Fine-Tuned Model. Once training completes, your model is automatically deployed to an endpoint. Use it like any other Gemini model:
pythonfrom vertexai.generative_models import GenerativeModel # Replace with your endpoint from the training job model = GenerativeModel("projects/PROJECT/locations/REGION/endpoints/ENDPOINT_ID") response = model.generate_content("Your prompt here...") print(response.text)
Key hyperparameters to consider: The adapter_size controls how many trainable parameters are added (1-8, higher = more complex learning but needs more data). Epochs of 3-5 are recommended for most tasks. According to the Google Cloud blog on fine-tuning best practices, start with defaults and only adjust if you see underfitting or overfitting in your evaluation metrics.
For detailed pricing information on Vertex AI fine-tuning and inference, check our Gemini API pricing guide.
Fine-Tune Gemma 3 for Free (Google Colab Guide)
This section shows you how to fine-tune Gemma 3 using Unsloth on Google Colab—completely free. This is the perfect starting point for learning or building prototypes.
Why Unsloth? According to their official blog, Unsloth makes Gemma 3 fine-tuning 1.6x faster with 60% less VRAM compared to standard implementations. Critically, they've solved compatibility issues with float16 precision on T4 GPUs, which means the free Colab tier actually works.
Step 1: Open the Notebook. Go to Unsloth's Gemma 3 Colab Notebook and open in Colab. Make sure to select the free T4 GPU runtime: Runtime → Change runtime type → T4 GPU.
Step 2: Install Dependencies. The notebook handles this, but here's what's happening:
python!pip install --upgrade --force-reinstall --no-cache-dir unsloth unsloth_zoo
Step 3: Load the Model. Unsloth provides pre-quantized models optimized for training:
pythonfrom unsloth import FastLanguageModel model, tokenizer = FastLanguageModel.from_pretrained( model_name="unsloth/gemma-3-4b-it", max_seq_length=2048, dtype=None, # Auto-detect load_in_4bit=True, ) # Add LoRA adapters model = FastLanguageModel.get_peft_model( model, r=32, # LoRA rank target_modules=["q_proj", "k_proj", "v_proj", "o_proj", "gate_proj", "up_proj", "down_proj"], lora_alpha=32, lora_dropout=0, bias="none", use_gradient_checkpointing="unsloth", )
Step 4: Prepare Your Data. Format your data as a list of dictionaries with input/output pairs:
pythonfrom datasets import Dataset # Your training data data = [ {"input": "Translate to French: Hello, how are you?", "output": "Bonjour, comment allez-vous?"}, {"input": "Translate to French: The weather is nice today.", "output": "Le temps est beau aujourd'hui."}, # Add 100+ more examples for best results ] # Create Hugging Face dataset dataset = Dataset.from_list(data) # Format for training def format_prompts(examples): return { "text": f"<bos><start_of_turn>user\n{examples['input']}<end_of_turn>\n<start_of_turn>model\n{examples['output']}<end_of_turn><eos>" } dataset = dataset.map(format_prompts)
Step 5: Train the Model. Configure and run training with the SFTTrainer:
pythonfrom trl import SFTTrainer from transformers import TrainingArguments trainer = SFTTrainer( model=model, tokenizer=tokenizer, train_dataset=dataset, dataset_text_field="text", max_seq_length=2048, args=TrainingArguments( per_device_train_batch_size=2, gradient_accumulation_steps=4, warmup_steps=10, max_steps=100, # Increase for better results learning_rate=2e-4, fp16=True, logging_steps=10, output_dir="outputs", ), ) trainer.train()
Training time varies: expect 10-20 minutes for 100 steps on a T4 GPU. The free Colab tier has session limits, so save your model after training.
Step 6: Save and Use Your Model. Save the fine-tuned model to Hugging Face or local storage:
python# Save locally model.save_pretrained("my-gemma-model") tokenizer.save_pretrained("my-gemma-model") # Or push to Hugging Face Hub model.push_to_hub("your-username/my-gemma-model")
VRAM Requirements by Model Size:
- Gemma 3 1B: ~4GB (fits on most GPUs)
- Gemma 3 4B: ~8GB (free Colab T4)
- Gemma 3 12B: ~24GB (Colab Pro or local A100)
- Gemma 3 27B: ~22GB with Unsloth optimizations (local A100 or better)
For getting started with Gemini APIs without fine-tuning, see our Gemini API key guide.
Fine-Tuning Costs and ROI Analysis
Understanding the true cost of fine-tuning helps you make informed decisions about where to invest your resources.
Vertex AI Costs: Training costs are calculated as: (tokens in dataset) × (epochs) × (price per million tokens). As of December 2025, Gemini 2.5 Flash training costs approximately $2-4 per million tokens. A typical fine-tuning job with 100,000 tokens over 4 epochs would cost $0.80-1.60 in training alone. Inference on your tuned model is charged at standard Gemini rates.
Gemma 3 Costs: Technically free if you use Colab or your own hardware. The hidden costs are your time and compute limits. Free Colab sessions last 12 hours maximum and may disconnect. Colab Pro ($10/month) gives you better GPUs (A100) and longer sessions. For production, you'll need to host the model yourself—cloud GPU instances range from $0.50-4/hour depending on size.
When is fine-tuning worth it? According to Google's best practices guide, fine-tuning makes economic sense when:
- You're making 1,000+ API calls per day on a specific task
- Prompt engineering requires >500 tokens of instructions each time
- You need consistent output format that prompting can't achieve
- Domain-specific accuracy is critical (legal, medical, technical)
Break-even analysis: If your current prompt uses 500 instruction tokens per call at $0.15/million (Gemini 2.5 Flash input), you're spending $0.000075 per call on instructions alone. At 1,000 calls/day, that's $2.25/month. A one-time fine-tuning cost of $5-10 can eliminate those instruction tokens, achieving ROI within a few months if the tuned model performs well.
Alternatives to consider: Before investing in fine-tuning, evaluate whether your needs can be met by prompt engineering, few-shot learning, or RAG. API aggregators like laozhang.ai offer free trial credits across multiple models, letting you test whether different base models solve your problem without fine-tuning. Sometimes a more capable base model with good prompting outperforms a fine-tuned smaller model.
FAQ and Troubleshooting
Q: Why can't I find Gemini 3 fine-tuning in Google AI Studio? A: Gemini 3 fine-tuning is currently only available to enterprise customers through Vertex AI. The public Gemini API (Google AI Studio) deprecated fine-tuning support in May 2025. Use Gemini 2.5 on Vertex AI or Gemma 3 locally instead.
Q: How many training examples do I need? A: Google recommends starting with 100-500 examples for optimal results. You can see improvements with as few as 20 examples for simple tasks, but more data generally produces better results. Quality matters more than quantity—clean, consistent examples outperform larger noisy datasets.
Q: My Vertex AI training job failed with "ResourceExhausted" A: This usually means you've hit quota limits. Check your quota for "Global concurrent tuning jobs" in the IAM & Admin console—it often defaults to 0 or 1. Request a quota increase or cancel existing jobs before starting new ones.
Q: Gemma 3 training crashes with "CUDA out of memory"
A: Reduce batch size to 1, enable gradient checkpointing, or switch to a smaller model. With Unsloth, try load_in_4bit=True for maximum VRAM efficiency. The 4B model should fit on 8GB GPUs, while 12B needs 24GB.
Q: Should I use full fine-tuning or LoRA? A: LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation) is recommended for most cases. It trains faster, uses less memory, and produces comparable results to full fine-tuning. Full fine-tuning is only needed for fundamental behavior changes requiring extensive retraining.
Q: My fine-tuned model is worse than the base model A: Common causes include overfitting (too many epochs on small data), inconsistent training examples, or format mismatch between training and inference. Try reducing epochs, cleaning your dataset, and ensuring your inference prompts match training format exactly.
Q: What's the difference between Gemini and Gemma? A: Gemini is Google's proprietary API model (closed source, cloud-hosted). Gemma is Google's open-source model family built on similar architecture (open weights, run locally). Gemma 3 matches or exceeds many proprietary models while being free to use and modify.
Q: Can I use my fine-tuned model commercially? A: For Vertex AI, yes—you own your fine-tuned model and can use it commercially. For Gemma 3, check the Gemma license—commercial use is permitted for most applications, but there are restrictions around specific use cases.
Summary
Fine-tuning Google's AI models in 2025 comes down to three realistic paths. Gemini 3 is the most capable but requires enterprise access. Gemini 2.5 on Vertex AI provides production-ready fine-tuning for businesses with cloud budgets. Gemma 3 offers the same technology for free, perfect for learning and prototyping.
For most developers, the recommended approach is to start with Gemma 3 on free Google Colab to validate your training data and approach, then scale to Vertex AI when you need production deployment with enterprise features. The data formats are compatible, making migration straightforward.
If you're unsure whether fine-tuning is right for your use case, consider starting with improved prompting techniques on base models. Services like laozhang.ai provide unified access to multiple AI providers with free trial credits, letting you experiment before committing to fine-tuning infrastructure.
The landscape continues to evolve quickly—Google has indicated that public API fine-tuning for newer models will return in the future. Keep an eye on the official Google AI documentation for updates.
![How to Fine-Tune Gemini Models: Complete 2025 Guide [Gemini 2.5 + Gemma 3]](/posts/en/how-to-fine-tune-gemini-custom-model/img/cover.png)